When it comes to protecting a home or business, few features are as important as siding. Beyond its role in shaping curb appeal, siding acts as the first line of defense against weather, moisture, and temperature changes. Whether you’re building a new property, upgrading an old one, or researching the best options for long-term durability, understanding siding is essential.
This guide explores everything you need to know about residential and commercial siding—materials, styles, benefits, installation tips, and maintenance practices.
Why Siding Matters
At its core, siding is more than just a decorative covering. It plays several critical roles:
-
Protection: Shields the structure from rain, snow, wind, UV rays, and pests.
-
Insulation: Many siding systems provide an extra thermal layer, reducing energy costs.
-
Durability: Preserves the structural integrity of walls by preventing moisture infiltration.
-
Curb Appeal: Enhances the appearance of the property, often increasing resale value.
-
Low Maintenance: Modern materials minimize the upkeep required to keep exteriors looking sharp.
Residential Siding: Making Homes Weather-Ready
Popular Residential Siding Materials
-
Vinyl Siding
-
Affordable, lightweight, and available in countless colors.
-
Resistant to rot, warping, and insects.
-
Excellent option for homeowners seeking a balance of cost and durability.
-
-
Fiber Cement Siding
-
A mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers.
-
Mimics the look of wood or stone but with greater fire resistance and longevity.
-
Requires professional installation due to its weight.
-
-
Wood Siding
-
A timeless option that brings warmth and natural beauty.
-
Available in clapboard, shakes, or shingles.
-
Needs regular sealing or painting to prevent moisture damage.
-
-
Engineered Wood Siding
-
Combines natural wood fibers with resin.
-
Offers the authentic look of wood with better resistance to decay.
-
More budget-friendly than traditional wood.
-
-
Metal Siding (Steel or Aluminum)
-
Durable, recyclable, and low-maintenance.
-
Great for homeowners in areas prone to harsh weather.
-
Often used in modern or industrial-style designs.
-
-
Stucco Siding
-
Made from cement, lime, sand, and water.
-
Popular in dry climates and offers excellent fire resistance.
-
Requires proper installation to prevent cracking.
-
Residential Benefits
-
Energy efficiency through insulated panels.
-
Customization with endless textures and finishes.
-
Property value boost due to modern, updated exteriors.
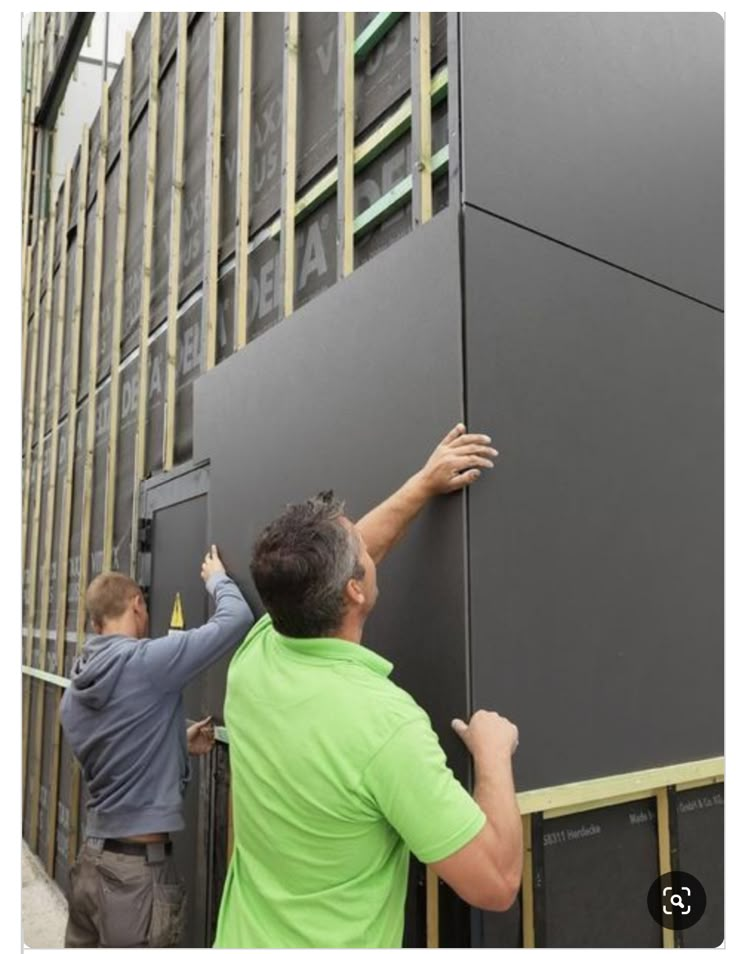
Commercial Siding: Durability Meets Design
While many of the same materials are used, commercial siding often emphasizes strength, fire resistance, and low maintenance.
Common Commercial Siding Choices
-
Metal Panels
-
Widely used for warehouses, office complexes, and retail spaces.
-
Provide long-term durability with minimal upkeep.
-
-
Fiber Cement Panels
-
Offer large, uniform panels for sleek, modern facades.
-
Fire-resistant and strong against heavy weather.
-
-
Brick and Stone Veneer
-
Adds prestige and permanence to commercial buildings.
-
Low maintenance and excellent durability.
-
-
Insulated Metal Siding
-
Combines thermal efficiency with weather resistance.
-
Reduces heating and cooling costs in large buildings.
-
-
Composite Materials
-
Blend metals, polymers, or resins for lightweight and long-lasting applications.
-
Commercial Benefits
-
Brand image: Sleek, professional exteriors signal reliability to clients and tenants.
-
Cost efficiency: Reduced energy bills and fewer maintenance interventions.
-
Longevity: Many commercial siding systems last 40–50 years.
Key Considerations When Choosing Siding
Whether for a home or a business, siding selection should account for:
-
Climate
-
Humid or rainy regions require moisture-resistant materials like vinyl or fiber cement.
-
Cold climates benefit from insulated siding that reduces heat loss.
-
-
Budget
-
Vinyl and engineered wood are cost-effective.
-
Natural stone and brick veneer are premium investments.
-
-
Maintenance
-
Low-maintenance options include metal, vinyl, and fiber cement.
-
Wood requires ongoing care.
-
-
Aesthetic Goals
-
Traditional homes may look best with wood or fiber cement.
-
Modern businesses may prefer sleek metal or composite panels.
-
-
Longevity
-
Some siding lasts 20 years, others 50+. Weigh upfront costs against long-term replacement.
-
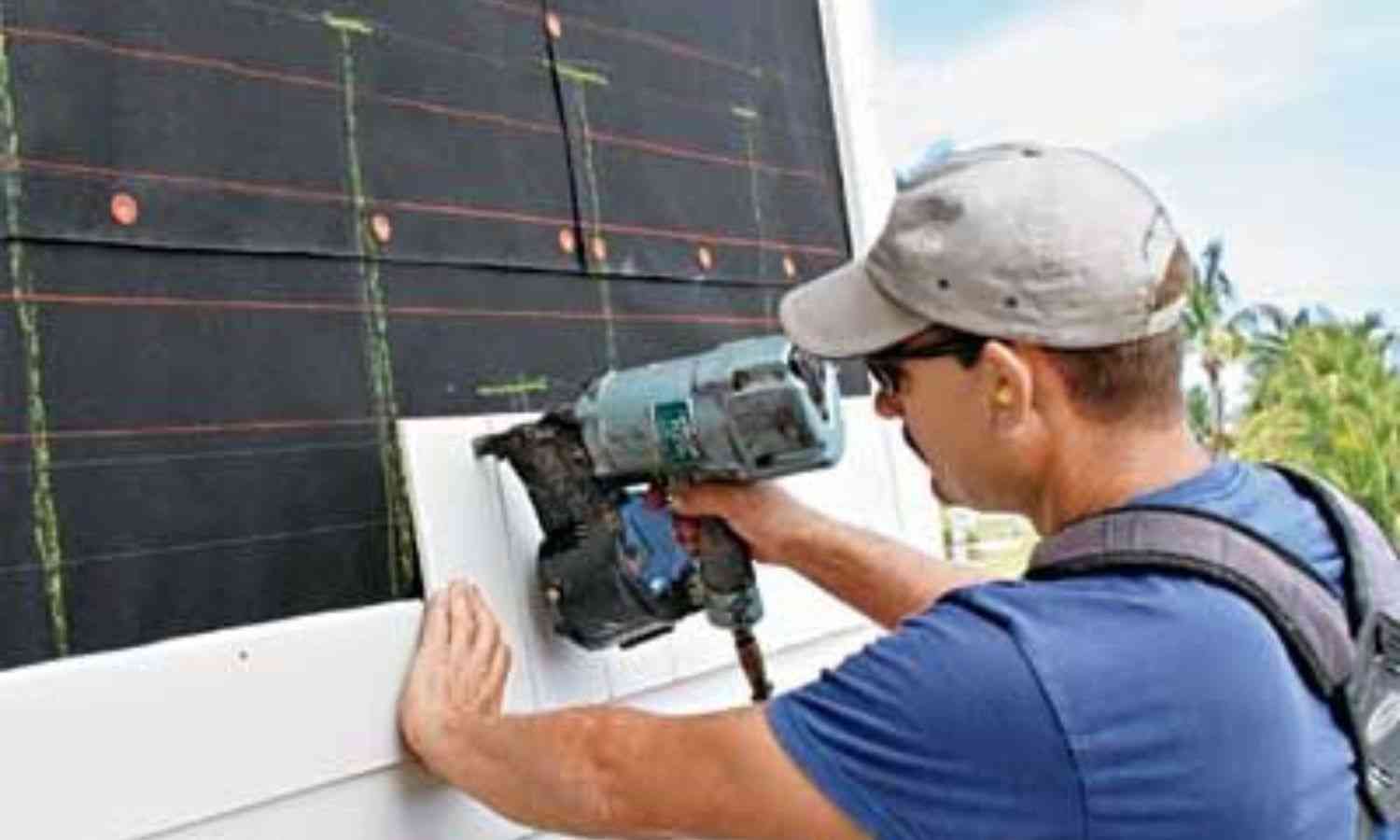
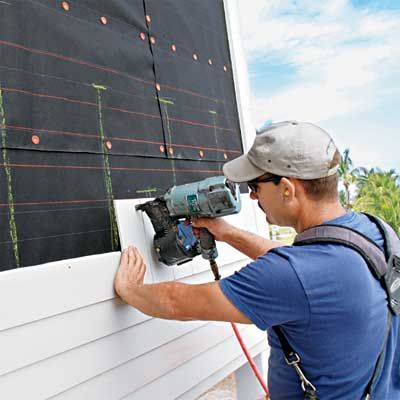
The Siding Installation Process
Steps Involved
-
Inspection and Preparation
-
Evaluate existing walls for moisture, rot, or damage.
-
Install weather barriers if needed.
-
-
Measuring and Cutting
-
Accurate measurements ensure minimal waste and clean alignment.
-
-
Attachment
-
Fastening siding panels or boards using nails, screws, or adhesives depending on the material.
-
-
Trims and Finishing
-
Corners, joints, and edges sealed for protection and aesthetics.
-
-
Clean-Up and Final Check
-
Inspection for gaps, unevenness, or exposed seams.
-
DIY vs Professional Installation
-
DIY may work for small projects using vinyl or wood, but mistakes can compromise protection.
-
Professional contractors bring expertise, warranties, and compliance with local building codes.
Siding Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance extends the life of siding and keeps it looking new.
-
Regular Cleaning: Power-wash vinyl and metal siding once a year.
-
Inspections: Check annually for cracks, gaps, or warping.
-
Sealing and Painting: Wood siding should be sealed or painted every 3–5 years.
-
Caulking: Keep joints and seams caulked to prevent water infiltration.
-
Prompt Repairs: Replace damaged boards or panels quickly to avoid structural issues.
Emerging Trends in Siding
Like all construction materials, siding is evolving with new technologies:
-
Sustainable Materials: More homeowners and businesses are choosing recycled or eco-friendly options.
-
Smart Siding: Some systems integrate with insulation and ventilation to improve energy efficiency.
-
Mixed Materials: Combining wood with metal or stone for unique modern aesthetics.
-
Bold Colors and Textures: Advances in manufacturing allow for long-lasting vibrant finishes.
Cost Considerations
Siding costs vary widely depending on material, labor, and building size.
-
Vinyl siding: $3–$8 per square foot installed.
-
Fiber cement: $6–$12 per square foot installed.
-
Wood siding: $8–$15 per square foot installed.
-
Metal siding: $7–$14 per square foot installed.
-
Stone veneer: $10–$20 per square foot installed.
Commercial projects typically involve higher upfront costs due to scale and durability requirements but yield long-term savings in maintenance and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Siding is more than a surface—it’s an investment in protection, efficiency, and design. From the cozy character of residential wood siding to the sleek durability of commercial metal panels, every option brings unique strengths.
For homeowners, the right siding enhances comfort, lowers utility bills, and boosts curb appeal. For businesses, it projects professionalism while cutting long-term costs. With proper selection, installation, and care, siding can last decades while safeguarding what matters most inside.
Whether you’re updating a family home or managing a large commercial property, siding remains one of the smartest exterior improvements you can make.