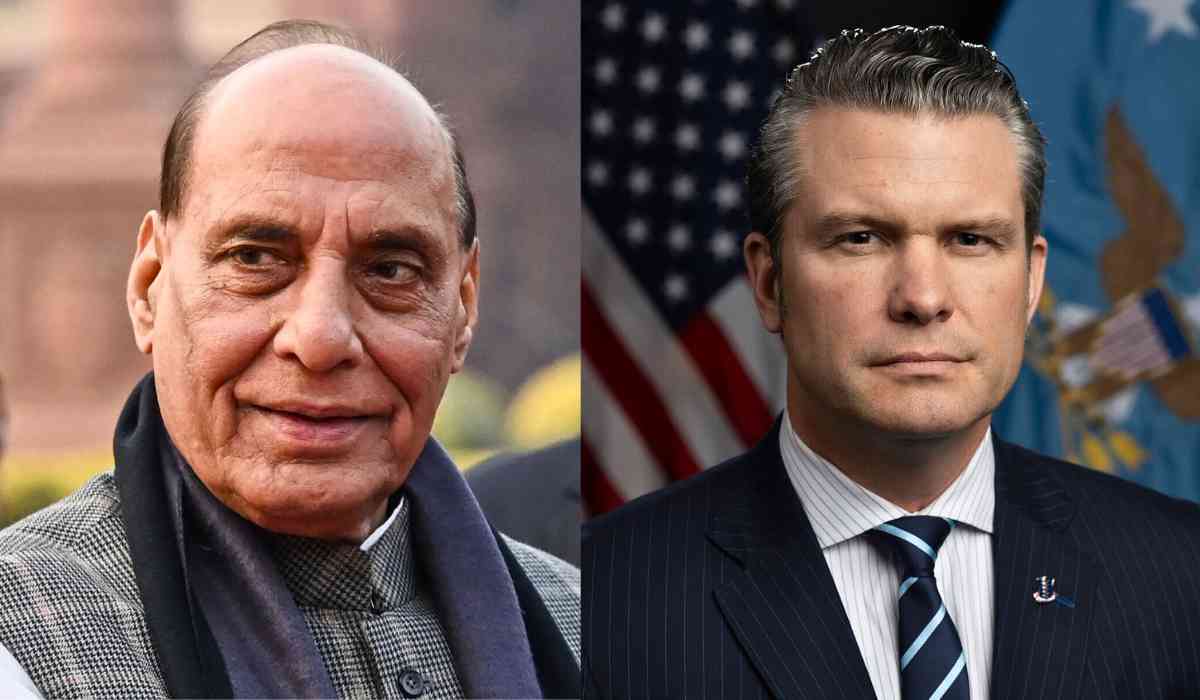
India and the United States are preparing to sign a 10-year defence cooperation framework agreement later this year. The framework—confirmed in phone talks between India’s Defence Minister Rajnath Singh and U.S. Secretary of Defence Pete Hegseth on July 1—aims to deepen military ties, enhance industrial cooperation, and strengthen security coordination between the two nations.

What the Framework Covers
-
Strategic and Operational Cooperation: The agreement will focus on expanding joint military exercises, intelligence sharing, logistics, and interoperability—helping both militaries operate smoothly together. The Pentagon stressed its role in enhancing coordination in the Indian Ocean and Indo‑Pacific region .
-
Defence Equipment & Sales: Major pending U.S. defense deals—such as engines (GE F404, F414), Apache helicopters, P-8I patrol aircraft, Javelin missiles, and Stryker vehicles—are expected to be finalized under this framework.
-
Industrial Cooperation & Co-Production: India is pushing for joint manufacturing inside the country. Discussions include building GE jet engines in India, collaborating with Indian firms like HAL and tapping initiatives such as INDUS‑X and the Defense Acceleration Ecosystem.
-
Technology Transfer & Innovation: Beyond hardware, the deal involves sharing emerging technologies like space capabilities, artificial intelligence, and drone systems. These are part of new defense dialogues and programs launched in recent years.
What India Stands to Gain
1. Modern Equipment and Reduced Reliance on Russia: India, which has long relied on Russia—accounting for around 49% of its defense imports—will diversify its defence supply chain. The U.S. offer of advanced aircraft, helicopters, drones, missiles, and engines could help India upgrade its forces with more reliable and modern tools.
2. Local Manufacture & Job Creation: Producing large-ticket items such as fighter engines and patrol aircraft in India supports Prime Minister Modi’s 'Make in India' and 'Atmanirbhar Bharat' goals. It could also spur employment and technology upskilling in India’s aerospace and defence sectors.
3. Boost to Indigenous Defence Industry: Cooperation in high-tech domains like AI, space systems, and drone technology may give Indian startups and research institutions fresh momentum. Partnering with U.S. firms through INDUS‑X and tech-focused frameworks is expected to accelerate innovation.
4. Enhanced Strategic Deterrence: Facing strategic pressure from China and Pakistan, India seeks to modernize its military. The new deal supports this by offering hardware and operational coordination to strengthen regional deterrence.
5. Leveraging the Quad and Regional Security: As part of its evolving role in the Quad, India benefits from defence cooperation that reinforces its presence in the Indo‑Pacific region. This long-term pact cements its partner status with the U.S. and other Quad nations.
Challenges and Considerations
-
Technology Control & Trust Issues: Export controls on sensitive U.S. military tech—like F‑35 systems—could delay or limit India’s access . Furthermore, India remains cautious of being overly dependent on any single supplier.
-
Procurement Delays: India has repeatedly raised concerns about delays in delivery—for instance, GE engines and Apache helicopters. The new framework must expedite these processes to be effective.
-
Preserving Strategic Autonomy: India’s non-aligned tradition means it won’t enter a formal military alliance. The framework must balance collaboration with India’s desire to chart its own foreign policy.

This framework represents a measured progression in India-U.S. ties. It is neither a defense treaty nor a military alliance in the traditional sense. Instead, it's a strategic pact—one that emphasizes mutual benefits like equipment access, regional stability, and industrial collaboration—while allowing India to maintain its independent posture.
Still, the success of the framework rests on timely implementation:
-
Will U.S. suppliers stick to delivery schedules?
-
Can India strengthen its regulatory and industrial systems to absorb new technologies?
-
How deeply will technology transfer and research cooperation really go?
The 10‑year span can give enough runway for investments and ecosystem development, but only if both sides follow through on commitments—especially in contract execution and industrial capacity-building.
In Summary
The 10-year India–U.S. defence framework signals a new chapter in defence cooperation:
-
India gets modern platforms, manufacturing uplift, tech innovation, and stronger deterrence.
-
The U.S. gains a reliable partner in Asia, increased defence trade, and influence in regional geopolitics.
-
Both nations benefit from co-development, shared training, better interoperability, and working together on global security issues.
If executed well, this deal could transform defence ties while still preserving India’s strategic independence. The details—factory rollouts, weapons deliveries, and joint technology projects—will shape the long-term impact.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.




_1751527561.jpg)