“The Earth is a fine place and worth fighting for.” — Ernest Hemingway
As we witness more intense wildfires, longer droughts, catastrophic floods, and unpredictable weather all around the world, the urgency of the climate crisis becomes impossible to ignore. The planet is heating up—and while many know about fossil fuels and deforestation, there are other surprising culprits behind this warming trend. Understanding these hidden drivers is crucial if we hope to solve the problem.
But before we dive into the lesser-known causes, let’s revisit the basics.

What is Global Warming?
Global warming refers to the long-term heating of Earth’s climate system due to human activities—primarily the burning of fossil fuels. Since the Industrial Revolution, the Earth’s average annual temperature has increased by a little more than 1°C (2°F).
-
Between 1850 and 1980, the temperature rose by about 0.07°C per decade.
-
Since 1981, that rate has more than doubled to 0.2°C per decade.
As a result, the last ten years have been the hottest on record. Rising temperatures trigger climate tipping points—like melting glaciers or thawing permafrost—that create feedback loops and cause even more warming.
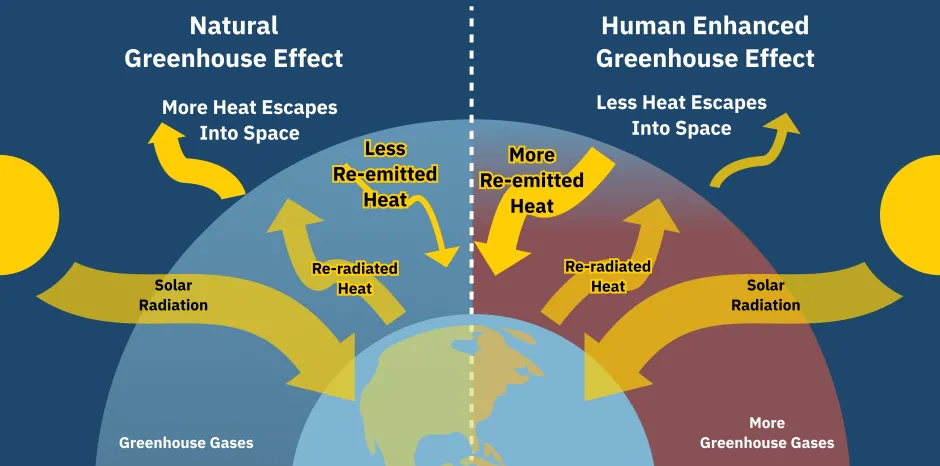
Global Warming vs. Climate Change: What’s the Difference?
While often used interchangeably, they are not the same:
-
Global warming is the rise in Earth's average temperature due to greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Climate change refers to the broader changes—like shifting weather patterns, rising sea levels, and more frequent extreme events—that result from global warming.
In essence, global warming is the engine, and climate change is the result.
Four Major Gases Fueling the Greenhouse Effect
At the heart of global warming lies the greenhouse effect—a natural process that traps some of the sun’s heat in Earth’s atmosphere. However, human activities have intensified this effect by releasing more of the following gases:
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Emitted from fossil fuel burning and deforestation.
-
Methane (CH₄): Comes from livestock, landfills, rice paddies, and fossil fuel leaks.
-
Nitrous Oxide (N₂O): Produced from fertilizers, combustion, and biomass burning.
-
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs): Industrial chemicals used in refrigerants and aerosols.
While water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, it acts as a feedback rather than a direct cause—warming oceans increase evaporation, adding more water vapor to the air and amplifying the warming effect.

10 Shocking Reasons for Global Warming That You Didn’t Know
Let’s move beyond the usual suspects and dive into surprising, underreported factors that are heating our planet.
1. Black Carbon from Cookstoves
Traditional biomass cookstoves used in rural areas emit black carbon (soot), a powerful short-lived climate pollutant. This soot settles on ice and snow, reducing their reflectivity and accelerating melting.
2. Livestock Feed Production
It’s not just cow burps (methane) that contribute to global warming—growing feed crops like corn and soy for livestock involves fertilizer use, land conversion, and energy-intensive agriculture that significantly add to greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Hydroelectric Dams
While considered a clean energy source, large reservoirs created by dams emit methane as submerged organic matter decomposes anaerobically, especially in tropical regions.
4. Refrigerant Leakage
HFCs (hydrofluorocarbons), used in air conditioners and refrigerators, are thousands of times more potent as greenhouse gases than CO₂. Even small leaks from appliances can have a significant climate impact.
5. Wetland Drainage
Draining wetlands for agriculture or development releases stored carbon dioxide and methane that would otherwise remain locked away in peat and soil.
6. Nitrogen-Based Fertilizers
Overuse of synthetic fertilizers leads to the emission of nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas nearly 300 times more potent than CO₂ over a 100-year period.
7. Mining and Rare Earth Extraction
Mining for metals and rare earth elements—especially those used in electronics and green technologies—disrupts soil carbon, consumes fossil fuels, and generates emissions during processing.
8. Excessive Cloud Seeding
Cloud seeding alters precipitation patterns and can lead to unexpected warming effects due to changes in cloud reflectivity and local climate balance, though it's still an area of active research.
9. High-Altitude Aviation
Airplane emissions at high altitudes create contrails and cirrus clouds, which can trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, contributing more to warming than the CO₂ alone.
10. Fast Fashion and Textile Waste
The fashion industry, especially fast fashion, contributes significantly through energy-intensive manufacturing, synthetic fiber use (which releases microplastics), and global shipping, all of which add to the carbon footprint.

Effects of Global Warming
The impacts of these hidden and well-known causes are all around us:
-
Rising Temperatures: Global temps have risen nearly 1°C since 1880, speeding up glacier melt and sea-level rise.
-
Ecosystem Threats: Coral reefs are bleaching and dying, disrupting marine biodiversity.
-
Unpredictable Weather: Droughts, floods, and superstorms are becoming the norm.
-
Disease Spread: Warmer temperatures enable mosquitoes and other vectors to spread diseases to new regions.
-
Higher Mortality Rates: Natural disasters, heatwaves, and health risks are increasing death tolls worldwide.
-
Loss of Natural Habitats: Changing climates are pushing species out of their homes, leading to migration or extinction.
So, What Can Be Done?
As we see extreme weather events growing—in number and in intensity—all around us, it is evident that climate change is a crisis that must be tackled. But in order to find the solutions, we must know the basics around global warming—and dig deeper into the hidden causes that silently fuel it.
Understanding that global warming has complex and often unexpected causes is the first step toward meaningful change. Solutions require:
-
Cleaner technologies and energy alternatives
-
Better agricultural practices that reduce methane and nitrogen emissions
-
Sustainable consumption, especially in fashion and food
-
Preserving natural carbon sinks like wetlands and forests
Every action matters. And every individual, community, and government must contribute.
Final Thoughts
The climate crisis is a puzzle with many pieces. The more we uncover, the better equipped we are to put together real, lasting solutions. These 10 unexpected causes show us that solving global warming requires more than cutting emissions from cars and power plants—it demands a global rethink of how we live, produce, and consume.
So, the next time someone asks “What causes global warming?”—don’t stop at CO₂. The truth is more complex—and more urgent—than we ever imagined.
Let’s not wait until the world is unrecognisable. Let’s fight for it now.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.