Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming industries across the globe, but perhaps nowhere is its impact more profound—and personal—than in healthcare. From diagnosing illnesses and personalising treatment plans to predicting patient outcomes and streamlining administrative tasks, AI is revolutionising how care is delivered and experienced.

What Is AI in Healthcare?
Artificial Intelligence in healthcare refers to the application of machine learning algorithms and software to simulate human cognition in the analysis, interpretation, and comprehension of complex medical data. Unlike traditional computing, AI is capable of learning from data, identifying patterns, and making decisions with minimal human intervention.
Healthcare AI systems are already being used to diagnose diseases, recommend treatment plans, assist in surgeries, and even predict survival rates. For instance, robotic surgical tools equipped with AI can help reduce physical fluctuations during surgery and provide real-time data to enhance surgical precision.
According to a 2019 study, 46% of healthcare organisations in the UK were already using AI technologies—an indicator of its widespread adoption. With the integration of AI accelerating, it’s poised to become a core pillar of digital health systems globally.
Current Situation of AI in Healthcare
Although AI in healthcare is still in its early stages in many regions, its adoption is expanding rapidly. Researchers, clinicians, and even patients are already experiencing its benefits. The COVID-19 pandemic showcased AI's potential in tracking disease spread, managing healthcare logistics, and even in drug development.
The integration of AI into healthcare systems promises not only to optimise workflows but also to democratise access to quality care—especially in under-resourced regions. As its capabilities continue to improve, AI is expected to become a vital component in modern medical infrastructure.

Types of AI in Healthcare
AI is a broad field encompassing several sub-technologies. In healthcare, the most commonly used types include:
-
Machine Learning (ML): Uses datasets (like electronic health records) to train algorithms capable of categorising information, predicting outcomes, and enhancing clinical decision-making.
-
Deep Learning: A more advanced subset of ML involving layered neural networks that can process larger and more complex data sets for tasks like image recognition in medical imaging.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Helps in understanding and interpreting human language, which is essential for analysing medical notes, documentation, research papers, and even patient feedback.
-
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Utilised to automate repetitive administrative tasks such as data entry, appointment scheduling, and billing, improving operational efficiency in hospitals
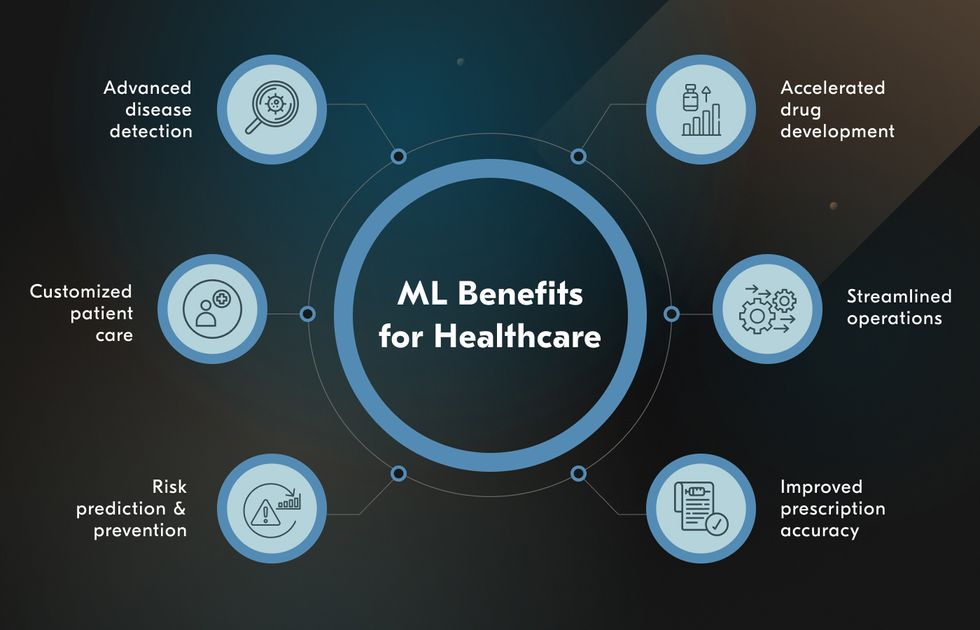
Advantages of AI in Healthcare
1. Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: AI can swiftly and accurately analyse large volumes of medical data, assisting doctors in diagnosing conditions more precisely and earlier than traditional methods.
2. Improved Patient Care: By reducing research time, minimising errors, and optimising treatment plans, AI helps clinicians offer more personalised and effective care.
3. Cost Efficiency: Automating administrative tasks and reducing the likelihood of diagnostic errors or unnecessary tests can significantly lower healthcare costs.
4. Real-Time Data Access: AI tools provide up-to-the-minute insights, enabling healthcare providers to make critical decisions swiftly, which is vital in emergency scenarios.
5. Reduced Workload and Stress: By taking over repetitive and time-consuming tasks, AI helps relieve healthcare workers’ burden, allowing them to focus on more critical and compassionate aspects of care.
6. Administrative Support: Tasks such as maintaining records, analysing scans, and processing paperwork are streamlined through AI, freeing up clinicians’ time for patient interaction.
7. Remote Monitoring and Digital Consultations: AI powers wearable devices and smart applications that track health metrics and facilitate telemedicine consultations, making healthcare more accessible and continuous.
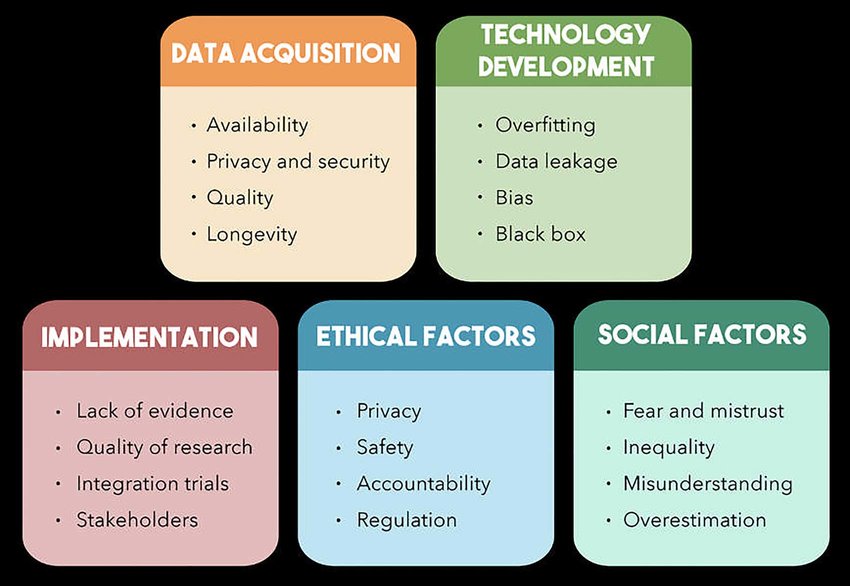
Disadvantages of AI in Healthcare
1. Training Challenges: Both healthcare professionals and AI systems require substantial training. Preparing curated datasets and ensuring user readiness can be time-consuming and complex.
2. Job Displacement Risks: AI may render certain roles—particularly administrative positions—redundant, raising concerns about employment in the healthcare sector.
3. Resistance to Change: Rapid technological shifts can be disruptive. Healthcare providers must be adequately prepared for AI integration to ensure safe and effective care.
4. Need for Human Oversight: While AI can analyse data efficiently, it lacks the emotional intelligence and intuition that human professionals bring to patient care.
5. Cybersecurity Concerns: AI systems are vulnerable to cyber threats, posing risks to sensitive patient data. Hospitals will need to invest heavily in cybersecurity infrastructure.
6. Social Context Limitations: AI struggles to consider socio-economic and cultural factors that may influence a patient’s condition or treatment suitability.
7. Possibility of Errors: Despite reducing human error, AI isn't immune to mistakes, particularly when working with incomplete or biased datasets.
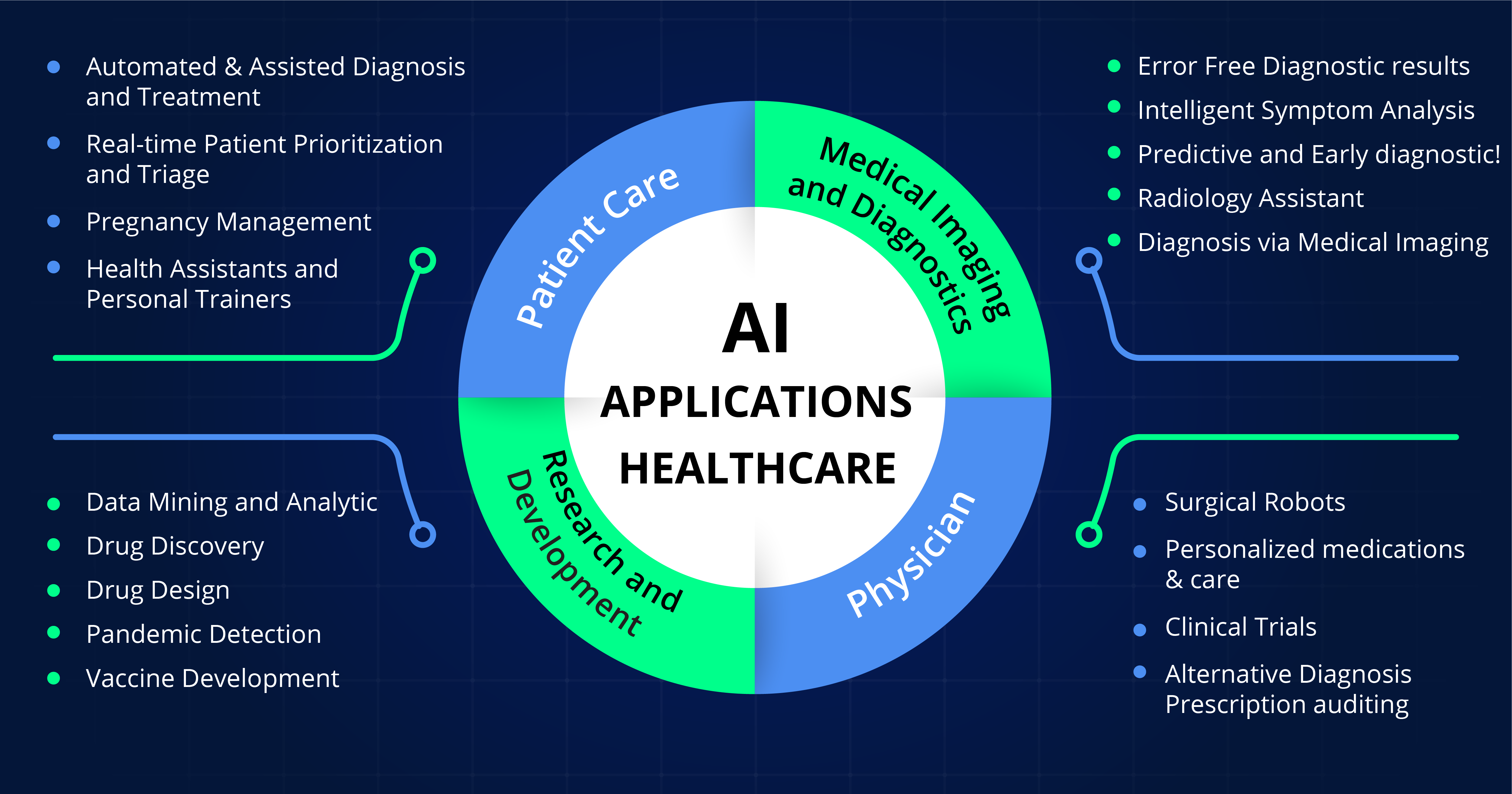
Applications of AI in Healthcare
AI is already making significant inroads into various medical domains. Some of the most impactful applications include:
-
Disease Detection and Diagnosis: AI algorithms can detect complex conditions, monitor disease progression, and alert healthcare professionals when intervention is needed.
-
Medical Imaging: AI models can analyse X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans as effectively as human radiologists, facilitating early diagnosis and reducing errors.
-
Drug Discovery and Development: AI accelerates the creation of new drugs by analysing existing compounds and predicting efficacy, significantly cutting down on time and cost.
-
Managing Medical Records: Efficient data collection and processing enable faster access to patient histories, supporting better treatment planning.
-
Improving Access to Care: AI bridges gaps in healthcare access by supporting professionals in under-resourced areas with diagnostic and decision-making tools.
-
Wearables and Remote Monitoring: Smart devices collect and transmit real-time health data, allowing for early detection of issues and remote management of chronic conditions.
-
Healthcare Analytics: ML models generate actionable insights by analysing historical data, leading to more informed decisions and better health outcomes.
-
Precision Medicine: By factoring in individual medical histories, genetics, and lifestyle choices, AI helps in crafting personalised treatment plans.
-
Predictive Modelling: AI predicts disease likelihood, enabling preventive interventions and reducing hospital admissions.
-
Test Interpretation: Trained algorithms can assess medical tests such as blood reports or imaging scans to deliver faster, more accurate diagnoses.
Real-World Examples of AI in Healthcare
AI is already making tangible impacts across the healthcare spectrum:
-
NITI Aayog (India): Using AI to detect diabetes early and screen for eye conditions.
-
Cancer Detection: AI models trained on mammograms now match or exceed human radiologists in accuracy.
-
COVID-19 Response: AI tools helped in tracking virus spread, vaccine development, and managing healthcare resources.
-
Virtual Consultations: AI-enabled platforms allow patients to consult with specialists remotely, improving healthcare access.
AI Jobs in Healthcare
As AI becomes more entrenched in the healthcare ecosystem, the demand for professionals skilled at the intersection of health and technology is soaring. Prominent AI-related roles in healthcare include:
-
Health Informatics Specialist
-
Machine Learning Engineer
-
Data Scientist
-
AI Engineer
These roles focus on designing, developing, and deploying AI tools to optimise healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes.

The Future of AI in Healthcare
The future of AI in healthcare is undeniably bright. While it’s not poised to replace medical professionals, it will increasingly support them in delivering high-quality care. From developing personalized therapies to unlocking new drugs and treatments, the potential is immense.
According to Grand View Research, the global AI in healthcare market is expected to grow at a
-
Global AI in Healthcare Market CAGR (compound annual growth rate) (2024–2030): 38.5%
-
India’s Projected Investment by 2025: USD 11.78 billion
-
Potential Economic Boost by 2035: USD 1 trillion
In the coming years, AI is expected to:
-
Support the discovery of new cures
-
Enhance diagnostics and treatment planning
-
Improve operational efficiencies in healthcare facilities
-
Expand access to care, especially in remote regions
As AI becomes embedded in digital health ecosystems, it will continue to improve healthcare efficiency, accessibility, and effectiveness. The vision is clear: a world where healthcare is not only smarter but more humane, precise, and proactive.
Final Thoughts
Artificial Intelligence is not just a buzzword—it’s an evolving technological force transforming the healthcare industry from the inside out. While it’s not without its hurdles, the potential benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. With careful implementation, proper training, and stringent data security, AI can enhance patient care, reduce operational inefficiencies, and help healthcare professionals do their jobs better and faster.
From predicting pandemics to personalising treatments, AI in healthcare represents the future—a future that is already here and continuing to evolve.
Whether you're a healthcare professional, a policymaker, or a curious patient, understanding the scope and significance of AI in healthcare is not just beneficial—it's essential.
As the line between medicine and technology continues to blur, AI will be at the heart of a healthcare revolution—offering a future where quality care is no longer limited by location, time, or human error.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.