When most people hear the word “blockchain,” their minds immediately jump to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. While blockchain technology underpins the success of digital currencies, its potential extends far beyond crypto markets. In fact, industries across the globe are now embracing blockchain for its transparency, security, and decentralization.
From supply chains to cybersecurity and even voting systems, blockchain is paving the way for more secure and efficient solutions.

What is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a distributed digital ledger composed of immutable, time-stamped records, called blocks, that are linked together using cryptographic techniques. Each participant in the network holds a copy of this ledger, which ensures transparency and reduces the risk of tampering.
Unlike traditional databases managed by centralized authorities, blockchain is decentralized. This key feature ensures that once data is entered into a blockchain, it cannot be altered retroactively without consensus from the network—making it extremely secure.
Key Benefits of Blockchain:
-
Decentralization: No single point of control
-
Immutability: Records cannot be changed once added
-
Transparency: Everyone in the network has access to the ledger
-
Security: Data is encrypted and protected by complex algorithms
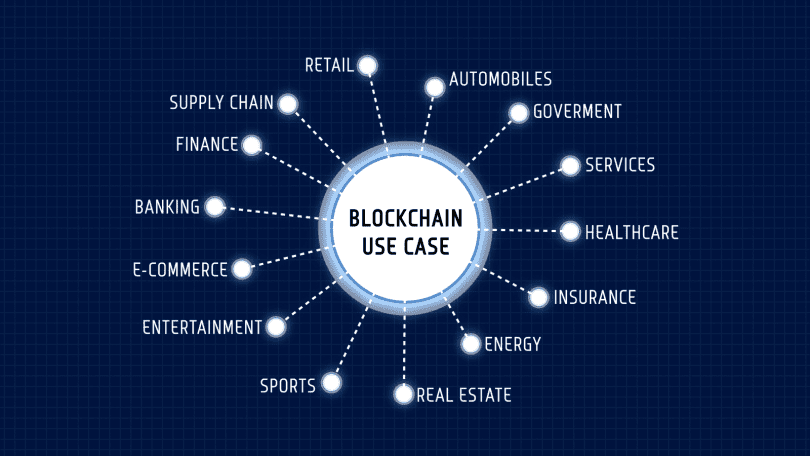
Blockchain in different industry
Clearly, demand for blockchain expertise is on the rise—and not just in crypto markets.
1. Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
One of the most impactful uses of blockchain is in supply chain management, where transparency and traceability are critical.
Real-World Example: Walmart and Food Safety
Imagine ordering apples online, only to receive them spoiled. With blockchain in place, each stage of the supply chain—from farm to consumer—can be tracked. This ensures the quality and freshness of goods upon delivery.
Walmart is leveraging blockchain in China to track the pork supply chain from farm to shelf. This distributed ledger enables all stakeholders—including farmers, shippers, and retailers—to access consistent, secure, and real-time data, reducing the risk of fraud or data manipulation.
Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chains
-
Improved traceability: Identify and eliminate weak links quickly
-
Reduced costs: Eliminate middlemen and manual data entry
-
Enhanced efficiency: Streamlined processes with less human intervention
-
Transparency: Real-time visibility for all participants
Example Supply Chain Flow with Blockchain:
-
Farm
-
Storage
-
Food Processing
-
Food Manufacturing
-
Distribution
-
Retailer
-
Consumer
Each step is recorded on the blockchain, making it easier to verify authenticity, monitor quality, and respond to issues like food spoilage or contamination.
2. Blockchain in Cybersecurity
The traditional internet model, which relies heavily on centralized cloud storage, is vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and identity theft. Blockchain addresses these weaknesses by decentralizing data and securing it with cryptographic methods.
Key Advantages of Blockchain for Cybersecurity:
-
High security: Immutable records make data tampering nearly impossible
-
Decentralized storage: No single point of failure
-
Lower transaction costs: Minimal reliance on third parties
-
Faster transactions: Real-time verification and processing
Real-World Example:
With blockchain, if Person A sends money to Person B, the transaction is distributed across the network and protected with cryptography, making unauthorized changes infeasible.
Mastercard utilizes blockchain technology to facilitate secure, peer-to-peer money transfers and currency exchange without a central authority, reducing the risk of hacking or fraudulent transactions.
3. Blockchain in Voting Systems
The integrity of elections is a major concern in many parts of the world. Centralized voting systems, including Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs), are often criticized for their vulnerability to tampering, leading to concerns about election integrity.
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary solution for fair, transparent, and tamper-proof voting.
How Blockchain Voting Works:
-
Voters download a blockchain-enabled app (e.g., MiVote)
-
Submit voter ID for verification
-
Cast their vote anonymously and securely
-
Vote is recorded on the blockchain and cannot be changed or erased
Real-World Example: MiVote
MiVote functions as a digital ballot box, allowing voters to participate in elections securely while preserving anonymity. Every vote is traceable, verifiable, and immutable, removing the need for third-party verification and minimizing fraud.
Benefits of Blockchain Voting:
-
Eliminates voter fraud and election rigging
-
Improves transparency and trust in elections
-
Reduces election costs
-
Allows voters to track their own votes
4. Blockchain in Financial Services
Blockchain is revolutionizing financial systems by improving transaction efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing security.
It has become such a big thing that some traders are now using Tokentact official website for their trades.
Key Financial Use Cases:
-
Settlement systems: Real-time trade settlements reduce back-office workload
-
Cross-border payments: Faster and cheaper international money transfers
-
Anti-fraud initiatives: Enhanced transparency reduces the risk of illicit activities
UBS Bank, for example, is exploring token-based solutions for international trades. Organizations like the Chamber of Digital Commerce and the Blockchain Alliance advocate for blockchain use in combating financial crimes while protecting data privacy.
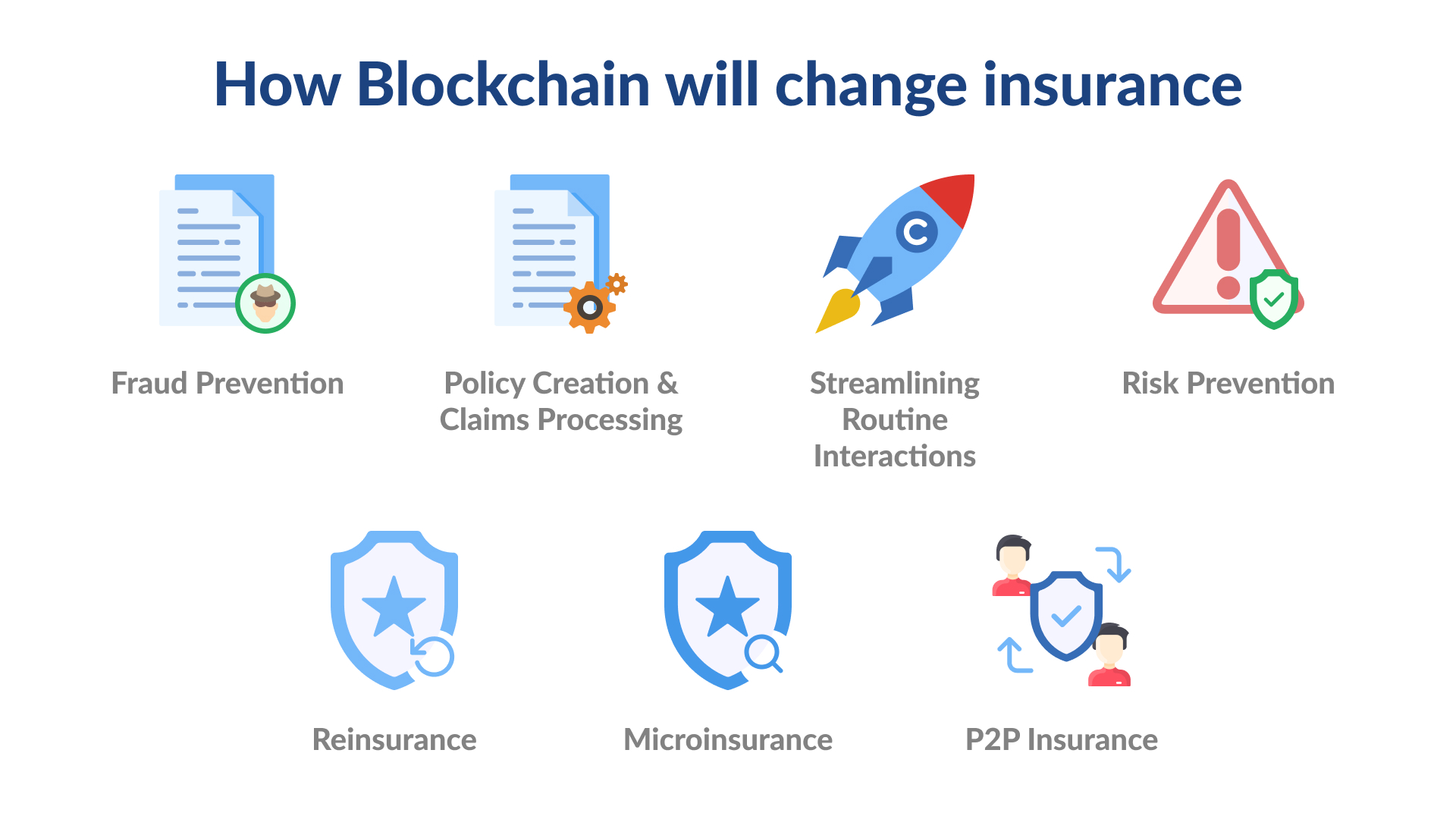
5. Blockchain in Insurance
Fraudulent claims are a major issue in the insurance industry. Blockchain enables secure and transparent data sharing between insurers, clients, and regulatory bodies.
Blockchain Benefits in Insurance:
-
Eliminates forgery and duplicate claims
-
Increases speed and efficiency of claim processing
-
Improves customer satisfaction through trust and transparency
With smart contracts, payouts can be automated based on pre-defined criteria, reducing administrative overhead.
6. Blockchain in Real Estate
Real estate transactions are traditionally time-consuming and require multiple intermediaries. Blockchain can streamline the conveyancing process, making it faster and more cost-effective.
Real Estate Benefits:
-
Instant and transparent property transfers
-
Reduced need for escrow and middlemen
-
Fraud prevention through verifiable property records
Smart contracts can automate lease agreements and title transfers, significantly reducing paperwork and legal hurdles.
7. Blockchain in the Music Industry
Artists and creators are turning to blockchain to gain greater control over their work and revenue.
Real-World Projects:
-
Mycelia by Imogen Heap: Helps artists manage distribution and rights
-
JAAK: Blockchain pilot for royalty payment tracking and distribution
Advantages for Musicians:
-
Automated royalty payments
-
Transparent licensing
-
Ownership protection
-
Efficient digital distribution
While widespread adoption is still underway, blockchain holds potential to resolve many long-standing issues in music rights management.
8. Blockchain for Weapons Tracking
Illegal arms trafficking is a significant global problem. Blockchain could create a transparent and immutable record of weapon manufacturing, sale, and ownership.
Proposed Use Case:
-
Global blockchain database: Tracks weapons from factory to owner
-
Immutable records: Prevent unauthorized resale or black-market transactions
-
Accountability: Authorities can trace illegal arms back to their origin
Each transaction in the weapon supply chain can be recorded securely on the blockchain, improving traceability and compliance with regulations.
9. Blockchain in Loyalty and Rewards Programs
Blockchain is streamlining customer rewards by replacing traditional loyalty cards with digital tokens.
Real-World Examples:
-
Gyft
-
Loyal
These platforms use blockchain to issue reward tokens instead of physical or digital gift cards, reducing fraud, eliminating waste, and cutting out the need for intermediaries.
Key Benefits:
-
Tokenized rewards: Easily tradable and secure
-
Fraud prevention: Immutable ledger prevents fake transactions
-
Eco-friendly: Reduces plastic and paper card usage
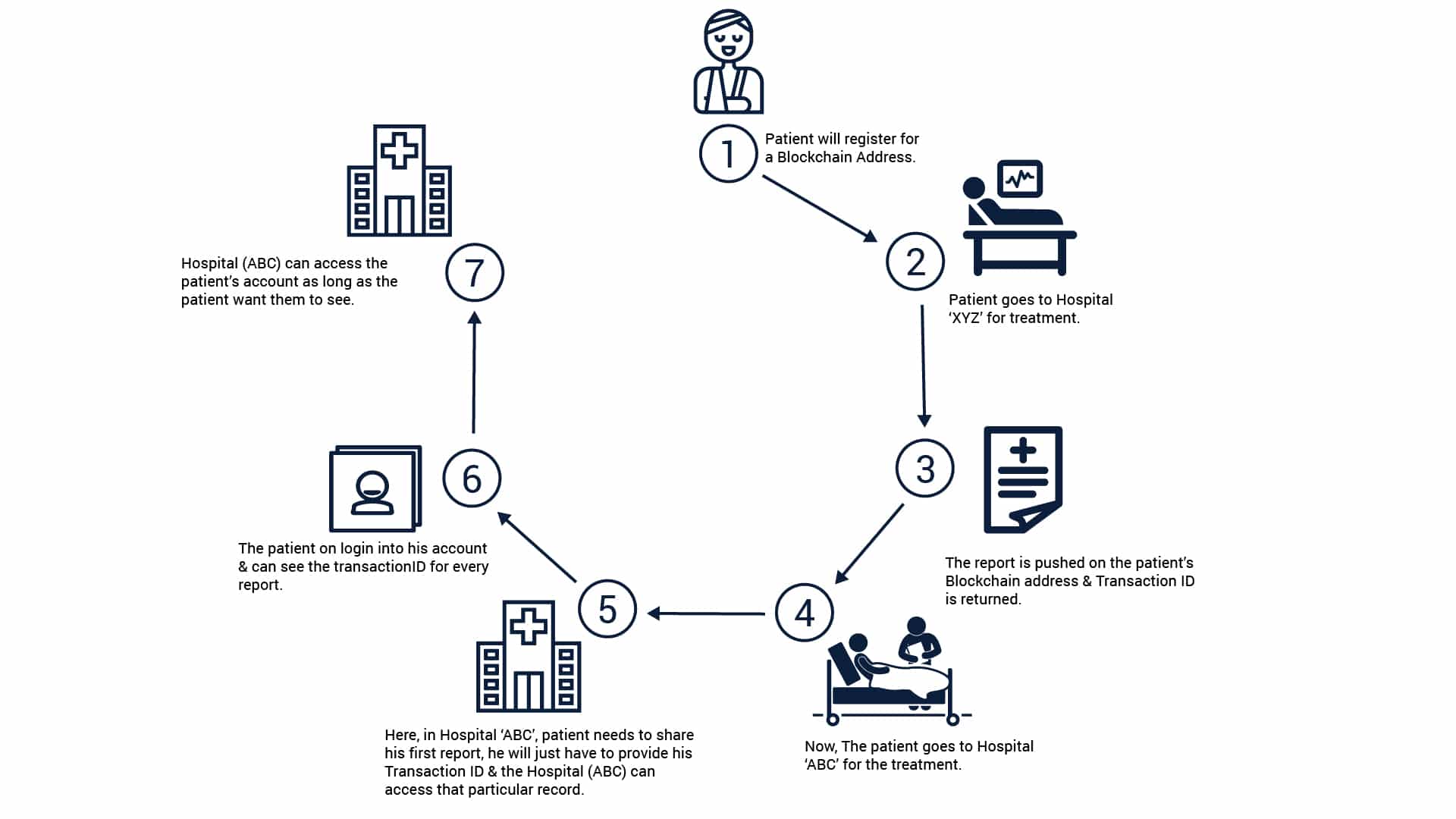
10. Blockchain in Healthcare
Healthcare providers are using blockchain to:
-
Maintain tamper-proof medical records
-
Secure patient data storage and sharing
-
Enhanced interoperability between healthcare providers
-
Reduced fraud in medical billing and insurance claims
Embrace Blockchain for a Better Future
The applications of blockchain go far beyond Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Its potential to transform supply chains, secure data, reform elections, and revolutionize industries is immense. As blockchain continues to evolve, mastering this technology can open doors to new career opportunities and business innovations.
Whether you're an IT professional, entrepreneur, or policymaker, understanding blockchain is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Blockchain isn’t just about Bitcoin—it’s about building the future.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.