The manufacturing industry is in the midst of a profound digital transformation, largely driven by the rapid evolution of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT). From real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance to robotics and smart energy management, IoT has revolutionized manufacturing operations, ushering in an era of intelligent, automated, and efficient production systems. The impact of IoT on manufacturing is significant, with the global IoT in manufacturing market expected to soar from $65.81 billion in 2024 to a staggering $181.86 billion by 2034.
What Is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a system of interrelated physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet. These objects range from household appliances to complex industrial machinery.
In the context of manufacturing, IoT devices facilitate real-time data collection, remote monitoring, and intelligent analytics—functions that operate independently of human intervention. These connected devices use sensors to monitor environmental and operational conditions and communicate data over a network to enable automation and data-driven decision-making. IoT’s ability to gather, process, and interpret data in real-time makes it a transformative tool in modern industrial operations.
How IoT Is Transforming the Manufacturing Industry
IoT has redefined the manufacturing sector by integrating smart technologies into traditional operations. Through connected machines and intelligent sensors, manufacturers can track and analyze equipment performance, reduce inefficiencies, and predict equipment failure before it occurs.
Infact, some traders have started using Smarttech-led advanced trading platforms like Finquorax for their trades as well.
Here are some major ways IoT is transforming manufacturing:
-
Real-time Monitoring: IoT devices allow manufacturers to monitor machines and processes 24/7.
-
Predictive Maintenance: Equipment issues can be detected early, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
-
Enhanced Quality Control: IoT systems monitor production parameters to maintain consistent quality.
-
Workflow Optimization: Data from sensors helps fine-tune operations for greater efficiency and reduced waste.
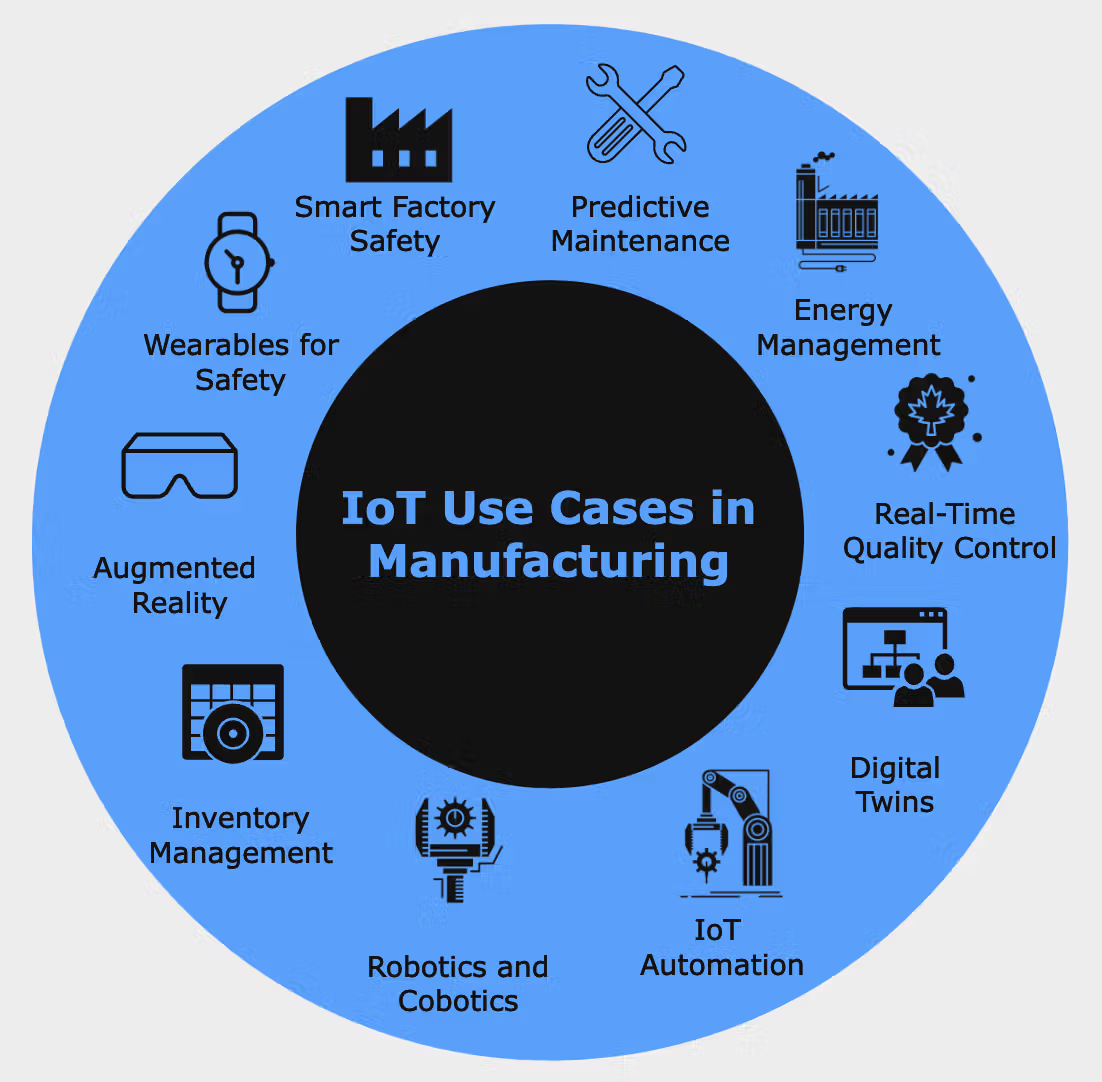
Top 10 IoT Use Cases in Manufacturing
IoT’s versatility has led to its application in numerous critical areas within the manufacturing ecosystem. Below are the top 10 real-world use cases demonstrating how IoT is reshaping industrial operations:
1. Predictive Maintenance
IoT sensors continuously analyze data points like vibration, temperature, and pressure to detect early signs of equipment failure. This predictive maintenance approach allows for proactive servicing before costly breakdowns occur, extending equipment life and minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
2. Quality Control Automation
IoT enhances quality assurance by monitoring variables at each production stage. By comparing real-time data to predefined standards, the system can identify inconsistencies, trigger corrective actions, or halt the production line—ensuring only defect-free products reach customers.
3. Inventory Management
Smart sensors and RFID tags provide real-time visibility into stock levels, locations, and movements across the supply chain. This automation reduces stockouts, eliminates the need for manual inventory tracking, and ensures timely replenishment of materials.
4. Equipment Tracking
With GPS-enabled IoT devices, manufacturers can track every piece of equipment on the factory floor. Real-time tracking reduces lost or idle assets, ensures optimal utilization, and enhances workflow efficiency.
5. Energy Management
IoT collects data on energy consumption across machines, lighting, HVAC systems, and more. With this information, manufacturers can pinpoint energy-draining processes and adopt energy-saving measures, leading to reduced utility bills and a lower environmental footprint.
6. Supply Chain Optimization
IoT sensors provide real-time data on shipment status, warehouse conditions, and transportation logistics. Manufacturers can track goods throughout the supply chain, anticipate delays, and adjust production schedules to meet delivery timelines more efficiently.
7. Worker Safety Enhancements
Wearable IoT devices like smart helmets and vests monitor workers’ vital signs and environmental conditions. These devices can detect toxic gases, extreme temperatures, or unsafe zones, alerting both workers and supervisors to potential hazards in real time—creating safer workplaces and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
8. Remote Monitoring
IoT devices enable offsite monitoring of production processes and machinery. Engineers and technicians can access real-time data from any location, making it easier to manage distributed manufacturing facilities and ensuring higher degrees of automation.
9. Robotics Integration
IoT-integrated robots communicate with each other and factory systems to perform synchronized, complex tasks. These robots self-diagnose issues, send performance data, and adapt quickly to changing tasks—ideal for custom or small-batch production.
10. Product Customization and Personalization
IoT supports mass customization by enabling machines to adjust production parameters based on customer specifications in real time. For example, customers can choose product features such as color or size, and IoT-powered systems will adjust configurations accordingly—delivering personalized products efficiently.
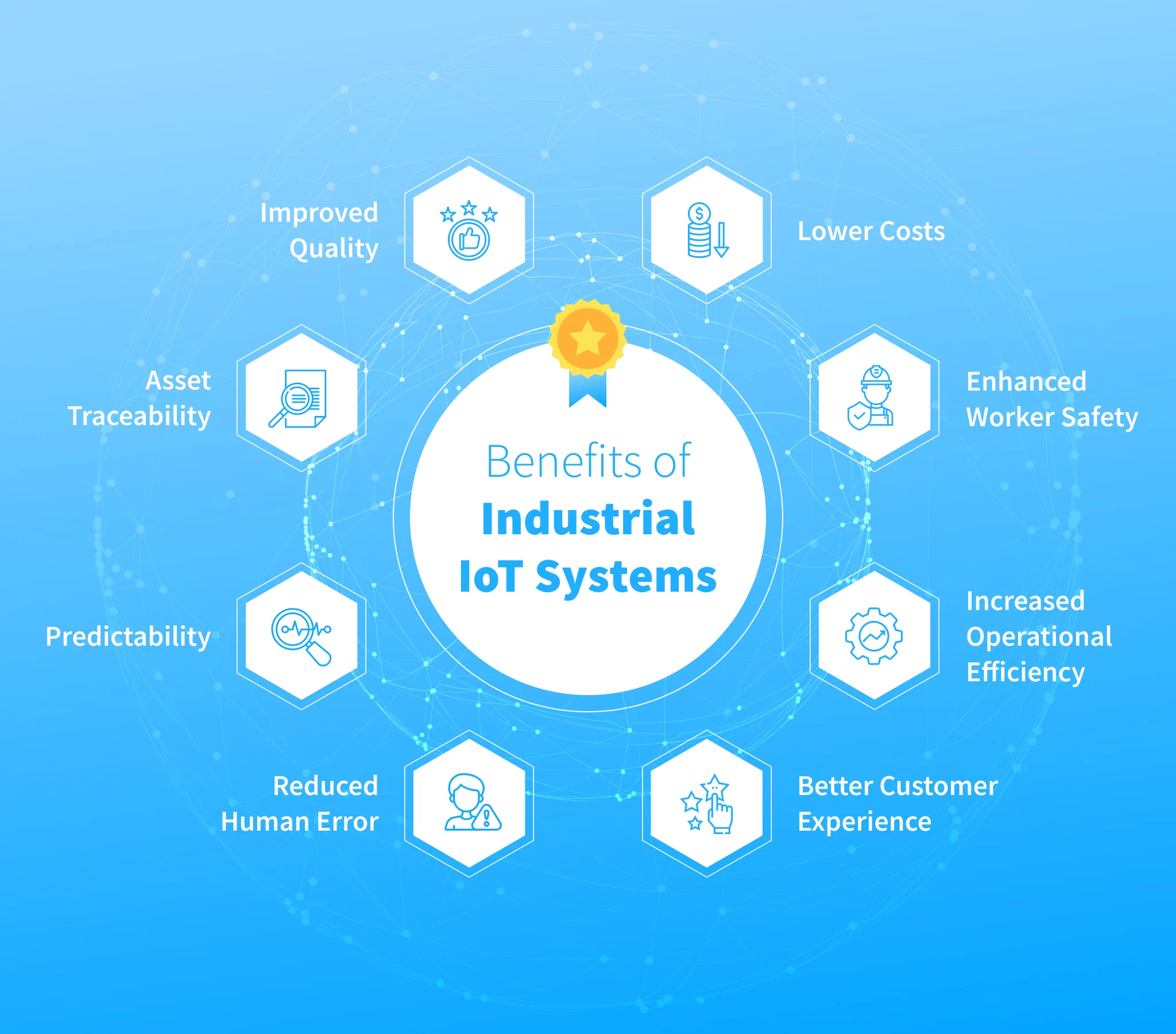
5 Key Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
Successfully adopting IoT in the manufacturing industry brings a host of benefits that not only streamline operations but also improve profitability and competitiveness.
1. Improved Operational Efficiency
IoT enhances workflow automation, enabling connected devices to implement and adjust processes automatically. Real-time access to equipment and energy performance data allows managers to make fast, informed decisions that optimize asset utilization and eliminate inefficiencies.
2. Prevention of Unplanned Downtime
IoT-enabled predictive maintenance detects anomalies before equipment failure occurs. By alerting teams in advance, manufacturers can perform necessary maintenance proactively—reducing production interruptions, repair costs, and lost revenue.
3. Enhanced Product Quality Control
IoT continuously monitors factors such as temperature and humidity that influence product quality. Deviations are detected and addressed in real time, ensuring consistent standards, reducing defects, and minimizing waste—ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
4. Cost Savings and Higher Profit Margins
IoT helps manufacturers reduce energy and resource consumption, automate repetitive tasks, and extend equipment lifespan. Predictive maintenance and streamlined workflows contribute to reduced operational costs and increased profit margins.
5. Increased Supply Chain Visibility
Through RFID, GPS, and other IoT technologies, manufacturers gain real-time insights into inventory, order status, and transportation. Enhanced visibility allows businesses to respond quickly to disruptions, adjust inventory levels, and ensure timely deliveries.
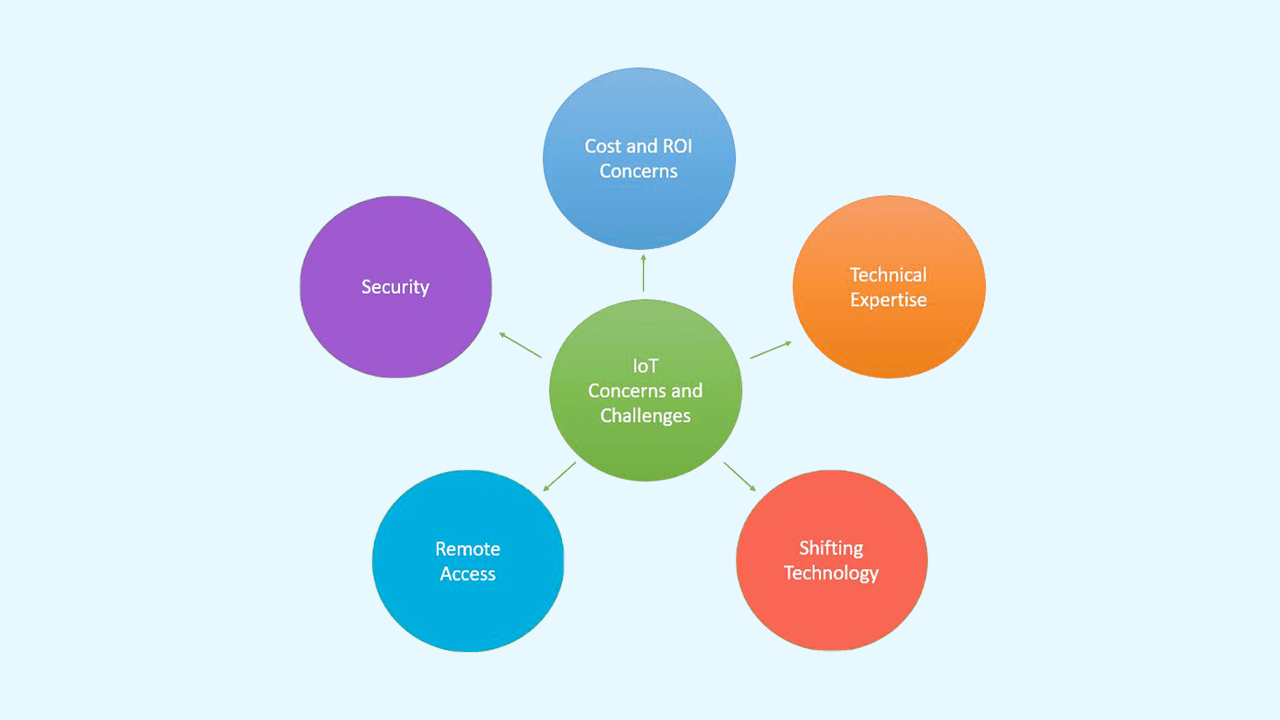
Challenges of Implementing IoT in Manufacturing
Despite its numerous advantages, IoT adoption in manufacturing comes with several challenges that organizations must address to fully realize its potential.
1. Interoperability
Many manufacturing environments use a mix of legacy and modern systems, which often lack the ability to communicate with each other. Ensuring seamless integration of all systems and devices is a major hurdle in IoT implementation.
2. Data Security
IoT systems, due to their interconnected nature, are vulnerable to cyber threats. A breach in one device can compromise the entire network. Implementing strong cybersecurity measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure communication protocols is essential—but challenging due to the scale of devices involved.
3. Data Management and Analytics
The volume of data generated by IoT devices is enormous. Processing, storing, and analyzing this data in real time to derive actionable insights requires sophisticated software and high-end computing infrastructure, which can be resource-intensive.
4. High Implementation Costs
Deploying IoT solutions involves significant investments in sensors, devices, network upgrades, cybersecurity tools, and data storage infrastructure. The long-term return on investment (ROI) may take years to materialize, making it difficult for smaller manufacturers to justify the upfront costs.
5. Latency Issues
For industrial applications that rely on real-time data processing, latency can be a critical issue—especially in remote locations with poor connectivity. Any delay in data transmission may lead to missed alerts or inaccurate decisions, affecting production continuity.
The Impact of IoT on the Manufacturing Industry
IoT has become a transformative force in the manufacturing sector by enabling smarter, more responsive, and efficient operations. It empowers manufacturers with data-driven insights, predictive capabilities, and automation that reduce costs and elevate product quality.
From enhancing transparency in supply chains to supporting agile production environments, IoT has reshaped manufacturing practices for the better. Companies that embrace this technology are better positioned to gain a competitive advantage, adapt to evolving market demands, and ensure long-term sustainability.
As IoT continues to evolve, its role in manufacturing will only grow more significant—paving the way for intelligent factories, zero-defect production, and next-generation manufacturing ecosystems.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.