India’s Economic Situation in 2025
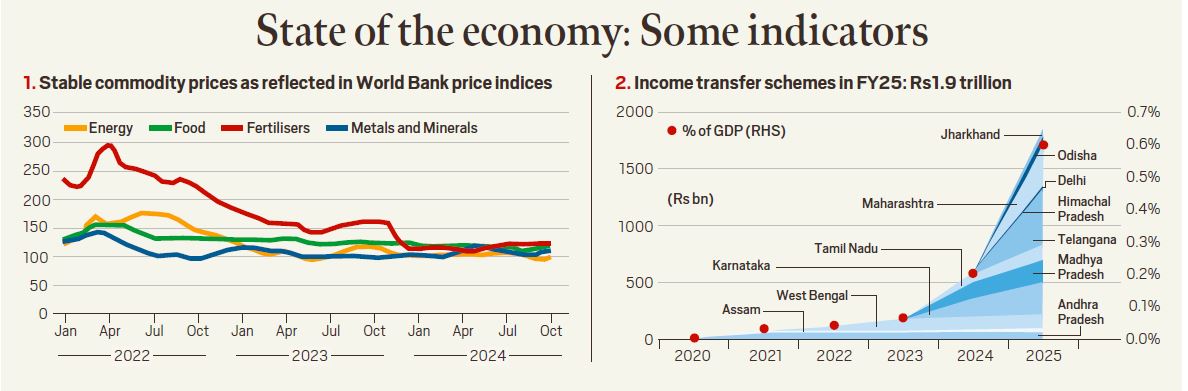
India’s economy in 2025 remains one of the fastest-growing among major global economies, despite a slight downward revision in growth forecasts. According to the latest projections from the United Nations and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), India’s GDP growth is expected to be between 6.2% and 6.3% for 2025, a modest reduction from earlier estimates but still outpacing most global peers. This robust growth is driven by resilient private consumption, strong public investment, and a thriving services export sector.
Key Economic Drivers
-
Private Consumption: Continued strength in household spending, especially in rural areas, supports economic momentum.
-
Public Investment: Government-led infrastructure and capital projects remain a major growth engine.
-
Services Exports: Sectors like IT, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and energy are performing well, even as merchandise exports face global headwinds.
Major Achievements and Global Standing
India is set to surpass Japan to become the world’s fourth-largest economy in 2025, with a nominal GDP of over $4.18 trillion. By 2028, India is projected to overtake Germany, becoming the third-largest economy globally. This ascent underscores India’s growing influence in the global economic landscape.
Inflation and Monetary Policy

Inflation in India is forecast to decline from 4.9% in 2024 to 4.3% in 2025, remaining within the Reserve Bank of India’s target range. This moderation has allowed the central bank to begin easing monetary policy for the first time in nearly five years, a move aimed at supporting growth amid global uncertainties.
Persistent Challenges
Despite its strong growth trajectory, India faces significant structural challenges:
-
Stagnant Job Growth: Unemployment remains stable, but job creation is not keeping pace with the expanding workforce, and gender disparities persist.
-
Food Inflation: Food prices continue to rise, with inflation rates exceeding 8%, impacting household budgets and overall consumption.
-
Trade Deficits: A widening trade gap and disappointing capital inflows present external vulnerabilities.
-
Manufacturing Slowdown: The manufacturing sector’s sluggish performance is a drag on overall growth, highlighting the need for deeper reforms.
-
Need for Reforms: Achieving higher, sustained growth rates (8% or more annually) necessary for developed-nation status by 2047 will require comprehensive economic reforms, particularly to attract foreign direct investment and boost manufacturing competitiveness.
Outlook and Opportunities

India’s economic fundamentals remain strong, and its role as a global growth driver is increasingly prominent. However, to fully realize its potential and maintain its growth leadership, India must address persistent challenges through targeted reforms and inclusive policies.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
©️ Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved. Powered by Vygr Media.