In today’s hyper-connected digital world, cybersecurity in the banking sector has evolved from being an IT concern to a critical pillar of financial stability. With billions of rupees and vast troves of sensitive personal and financial data at stake, Indian banks are under relentless pressure to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated cybercriminals. Cybersecurity is no longer optional—it is the backbone of trust, compliance, and continuity in modern banking.

What is Cybersecurity in Banking?
Cybersecurity in banking encompasses a comprehensive set of technologies, protocols, and practices aimed at safeguarding digital financial infrastructure from cyber threats. This includes protecting everything from online banking portals and mobile apps to internal data systems and transaction networks.
The core objectives of cybersecurity in banking are:
-
Confidentiality – Ensuring that sensitive data, such as customer information and transaction details, remains private.
-
Integrity – Guaranteeing that data is accurate and has not been altered or tampered with.
-
Availability – Keeping banking systems accessible and operational at all times, even during attempted cyberattacks.
Banks handle vast amounts of sensitive data daily, including customer identification details, financial records, and account activity logs. Securing this information from breaches, hacking attempts, malware, and insider threats is essential to maintaining customer trust and regulatory compliance.

Why is Cybersecurity Important in Banking?
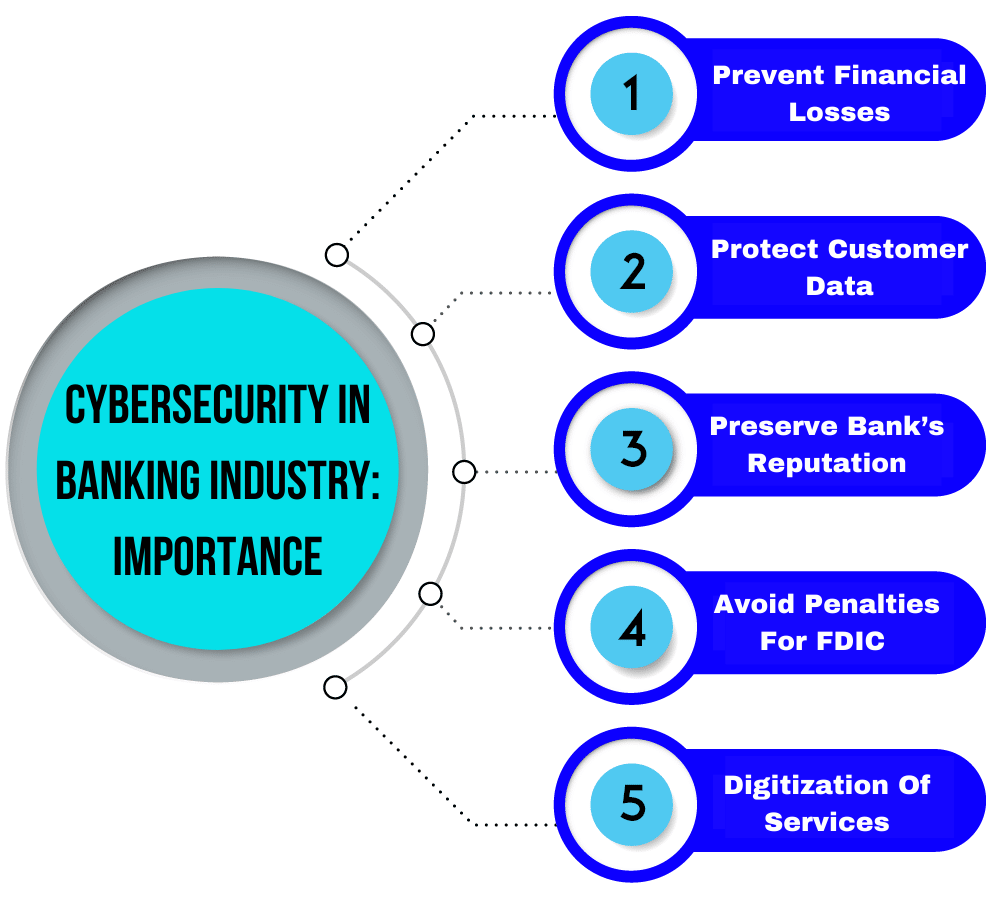
1. Protecting Customer Data
Banks serve as custodians of personal and financial data, including PAN numbers, Aadhaar details, account information, and transaction histories. A breach can lead to identity theft, fraud, and significant financial losses. Technologies like encryption, firewalls, and secure login systems ensure that unauthorized individuals cannot access this sensitive information.
2. Maintaining Trust and Credibility
Trust is foundational in banking. Customers expect their financial institutions to protect their data and funds. Any cyber breach can erode customer confidence and lead to reputational damage, potentially causing massive customer attrition.
Infact to make experiences better, traders have started using platforms like grokaitrading.com for better trade efficiency.
3. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Banks must comply with rigorous data protection regulations such as the RBI's cybersecurity framework, GDPR (for global operations), and local IT Act provisions. Non-compliance can result in heavy fines, legal action, and the loss of operational licenses.
4. Preventing Financial Losses
Cyberattacks like ransomware or account breaches can lead to direct monetary losses. Additionally, banks may have to compensate affected customers, pay for system recovery, and endure service outages, all contributing to heavy financial burdens.
5. Safeguarding Critical Infrastructure
Cybersecurity measures protect essential banking platforms such as ATMs, mobile apps, and payment gateways. A breach could bring these services to a halt, affecting thousands of customers and causing massive operational chaos.
6. Ensuring Business Continuity
Robust cybersecurity ensures that banks can recover swiftly from attacks. Disaster recovery systems, regular data backups, and incident response plans help minimize downtime and ensure uninterrupted customer service.
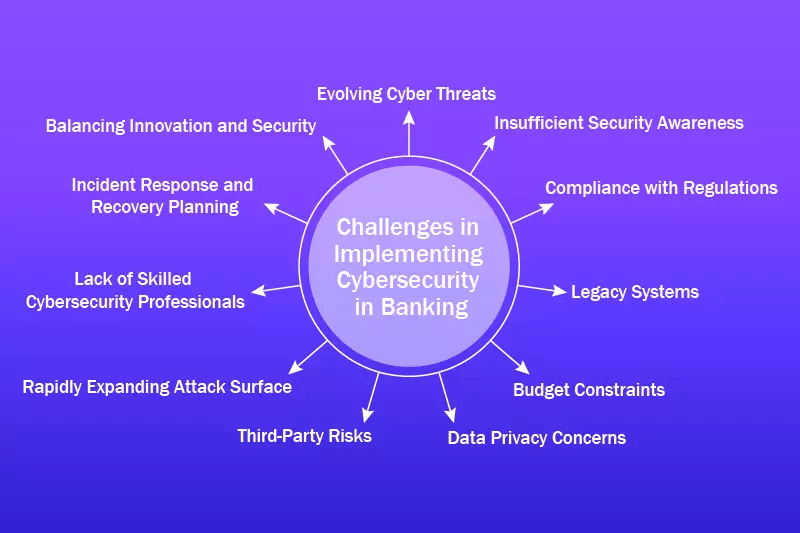
Threats and Challenges to Cybersecurity in Banking
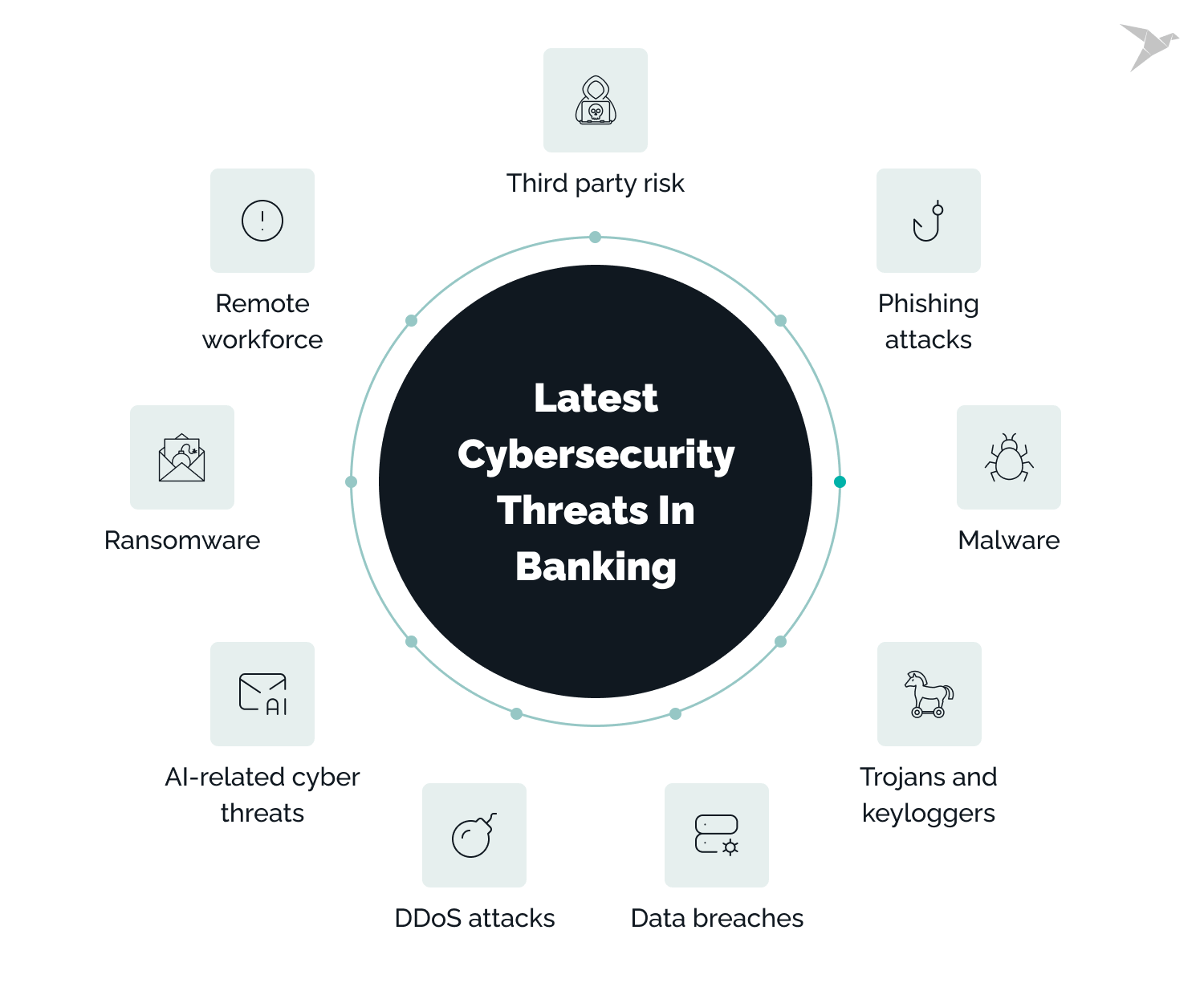
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing remains a top threat. Cybercriminals impersonate legitimate sources through deceptive emails, messages, or websites to extract login credentials and personal information.
Real-World Example:
In 2024, a massive phishing scam targeted Australian bank customers through fake emails. Many individuals were duped into sharing sensitive data, resulting in substantial financial losses and raising alarms across the financial sector.
2. Malware and Ransomware
Malware infiltrates systems to steal data or disrupt operations. Ransomware specifically locks users out of systems, demanding payment to restore access.
Real-World Example:
The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack infected banking systems worldwide, forcing several institutions to pay ransoms or suffer prolonged service outages.
3. Insider Threats
Employees or contractors with privileged access may accidentally or maliciously compromise security. Managing insider risks is complex and requires strict access control policies.
Real-World Example:
In 2019, a former Amazon employee hacked Capital One’s cloud servers, exposing the personal data of over 100 million customers. This breach cost the bank heavily in legal penalties and reputation.
4. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks flood banking websites with traffic, crashing systems and disrupting services like online banking.
Real-World Example:
In 2022, several major UK banks were hit by DDoS attacks, leaving thousands of customers unable to access their accounts for hours and severely impacting customer satisfaction.
5. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
These long-term, stealthy attacks target banks to extract data gradually while evading detection.
Real-World Example:
In 2016, hackers attempted to steal $1 billion from Bangladesh’s central bank via the SWIFT system. Although most of the money was recovered, $81 million was lost—highlighting how even central banks are not immune to APTs.
6. Third-Party and Supply Chain Attacks
Banks rely on external vendors for various services, creating weak entry points. A breach at a vendor level can cascade into the bank’s system.
Steps to Follow to Protect Yourself from Cyber Issues
Bank customers must also take proactive steps to secure their financial information:
-
Use Strong Passwords
Create complex passwords using a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using names, birthdates, or common phrases. -
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Adds an extra layer of verification, such as biometrics or one-time codes. -
Stay Vigilant Against Phishing
Don’t click on links or attachments in unsolicited emails or texts. Verify the source before sharing any information. -
Update Software Regularly
Ensure that your banking apps, OS, and antivirus software are up to date to protect against known vulnerabilities. -
Monitor Account Activity
Frequently review statements for unauthorized transactions. Report suspicious activity immediately. -
Secure Your Devices
Use firewalls, antivirus tools, and avoid using public Wi-Fi for online banking. -
Educate Yourself
Stay informed about the latest cyber threats and safe digital banking practices. -
End-to-End Encryption
Ensure your bank uses strong encryption protocols for data protection during transmission and storage. -
AI-Powered Threat Detection
Banks now leverage artificial intelligence to monitor for anomalies and respond to threats in real time. -
Zero Trust Architecture
This security model verifies every user and device, preventing lateral movement by attackers within a network. -
SIEM Systems
Security Information and Event Management systems aggregate data from multiple sources to provide real-time threat alerts.
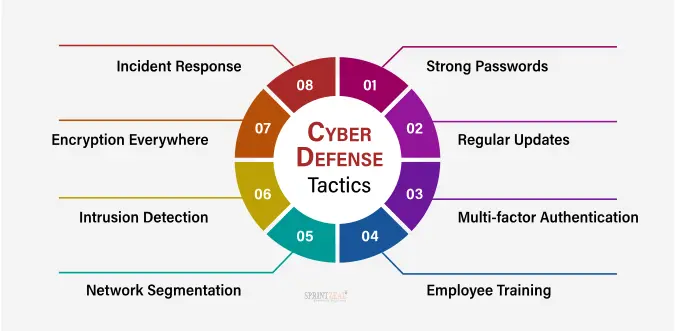
Best Practices for Cybersecurity in Banking
To stay secure in an ever-evolving threat landscape, banks must adopt industry-wide best practices:
-
Regular Employee Training
Educating employees to recognize and report phishing attempts and follow security protocols is crucial. -
Conduct Routine Security Audits
Periodic reviews of systems help identify and fix vulnerabilities. -
Keep Software Updated
Patching outdated systems closes doors that hackers could exploit. -
Enforce Strong Password Policies
Encourage the use of unique passwords and regular changes. -
Develop a Cyber Incident Response Plan
A clearly defined plan helps banks respond quickly and limit damage in the event of an attack.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Banking
Looking ahead, the future of cybersecurity in banking will be shaped by both technological advancement and regulatory enforcement.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML) will play a critical role in identifying threats based on behavioral patterns and automating responses in real time.
-
Blockchain Technology could enhance transaction security through decentralization and immutability, making financial systems more transparent and tamper-proof.
-
Quantum Computing—while still in its infancy—may revolutionize encryption methods, either strengthening cybersecurity or posing new challenges.
-
Stricter Regulations from national and international bodies will enforce higher standards for data protection and cyber resilience, compelling banks to evolve rapidly.
In a world where digital financial services are becoming the norm, the focus on cybersecurity will only intensify. It will require a proactive, multi-layered approach involving cutting-edge technology, rigorous compliance, and active customer participation.
Final words
Cybersecurity in the Indian banking sector is not just a technical requirement—it is a critical pillar for trust, safety, and economic stability. As cyber threats grow more advanced, both banks and customers must work together to stay secure. From adopting strong internal security protocols to practicing safe banking habits, every step taken towards cybersecurity creates a stronger, more resilient financial system for everyone.
Whether you're a banking professional, regulator, or everyday customer, understanding the importance of cybersecurity and implementing best practices can make all the difference in building a safer digital banking environment.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.