Green technology, or green tech, refers to environmentally friendly innovations designed to minimize the negative impacts of human activity on the planet. These technologies promote sustainability by improving efficiency, reducing waste, and conserving natural resources. Whether it's clean energy, electric vehicles, or sustainable agriculture, green tech is increasingly recognized as essential to combating climate change and environmental degradation.

Understanding Green Tech
Green tech is an umbrella term encompassing scientific and technological advancements aimed at protecting and preserving the environment. It overlaps with cleantech, which focuses on improving operational efficiency while reducing environmental harm and lowering costs. Green technology is also known as environmental technology or eco-technology, focusing on creating solutions that conserve natural resources, reduce pollution, and enhance the ecological balance.
The primary goals of green tech are to:
-
Conserve Earth's natural resources,
-
Prevent further environmental damage,
-
Remediate damage caused by industrial and human activity.
Green tech has become a strategic priority for many organizations and investors. Companies often outline their environmental initiatives in Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reports or even their mission statements. As a result, many socially conscious investors now focus exclusively on businesses that employ or develop green technologies.
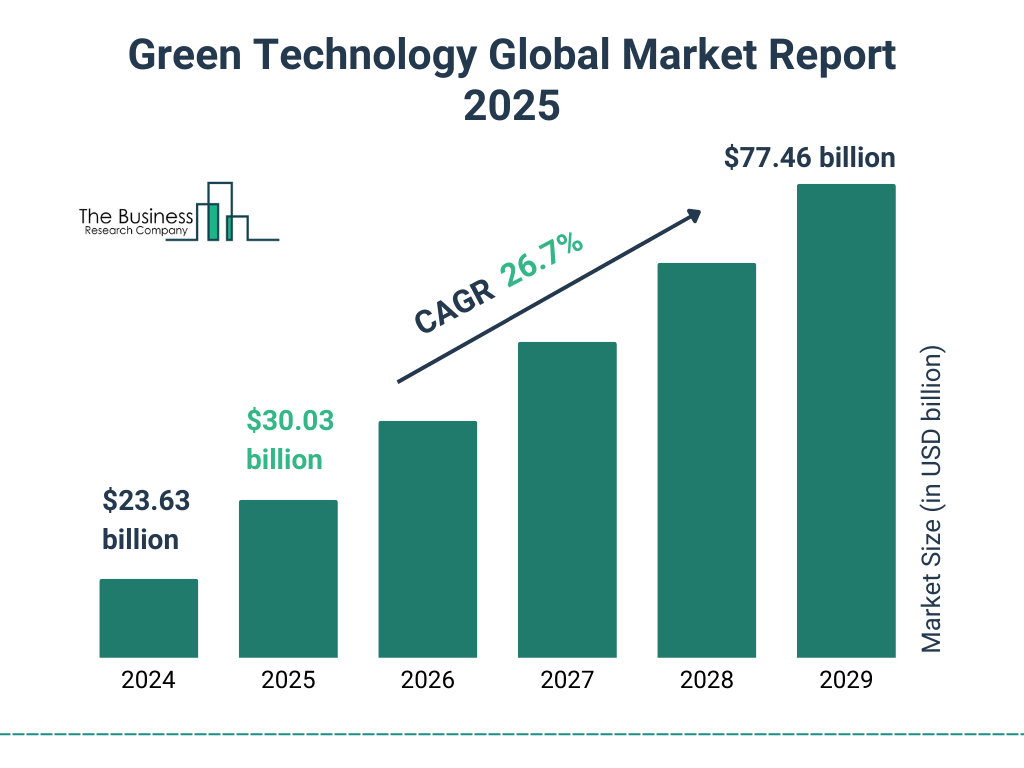
As environmental concerns such as climate change, resource depletion, and pollution continue to intensify, green technology has garnered significant attention and investment. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy sources accounted for nearly 28% of global electricity generation in 2020, a substantial rise from 22% in 2010. This growth showcases the increasing adoption of green technologies globally.

A Brief History of Green Tech
While green tech has gained prominence in recent years, its roots date back to the Industrial Revolution, when scientists first observed the environmental impacts of coal-based industries. Key historical milestones include:
-
World War II: Over 400,000 U.S. volunteers collected metals, paper, and rubber to reduce consumption and waste.
-
1960s–70s: Public awareness grew around the dangers of pesticides and radiation. Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring and nuclear fallout reports marked the rise of the ecological movement.
-
1970: The U.S. established the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which began regulating pollution and promoting clean technologies.
Since then, awareness and innovation have accelerated, laying the groundwork for today's robust green tech industry.
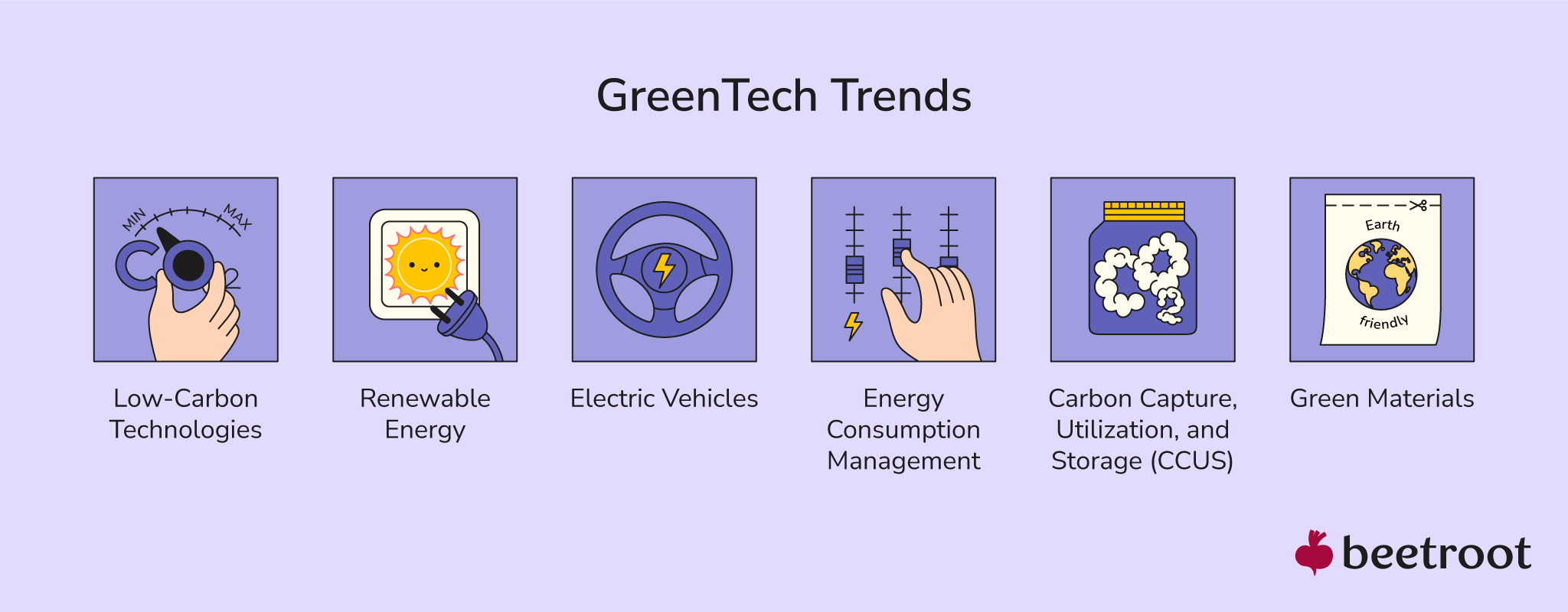
Types of Green Tech
Green technology is a broad field encompassing various solutions to environmental challenges. Here are some key types of green tech:
-
Alternative Energy: Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy are among the most prominent alternatives to fossil fuels. Solar power, in particular, has become one of the most affordable energy sources globally.
-
Electric Vehicles (EVs): EVs significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and pollution compared to traditional vehicles. However, challenges like battery efficiency, infrastructure development, and energy grid reliance remain.
-
Sustainable Agriculture: This includes practices such as organic farming, precision agriculture, and vertical farming, aiming to minimize environmental impact while ensuring food security.
-
Recycling Technologies: Recycling involves reusing materials to conserve natural resources and reduce waste. Advanced recycling processes also recover valuable materials from e-waste and other specialized products.
-
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS): CCUS technologies capture carbon dioxide emissions from industries and either store them underground or use them in other applications, helping to mitigate climate change.

Adoption of Green Tech
Adoption varies by technology and region. Major trends include:
-
Plastic reduction: Many nations are banning single-use plastics, prompting innovation in biodegradable materials.
-
Energy transition: The U.S. Energy Information Administration projects that 71% of new energy capacity in 2024 will come from wind and solar.
-
Global investment: Cumulative investment in renewable energy surpassed $3 trillion in 2024.
Singapore is among the leaders, targeting a 70% recycling rate by 2030.
Key Areas Within Green Tech
Several core areas within green technology are driving significant change. These include:
-
Renewable Energy: Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy technologies are crucial to replacing fossil fuels and reducing carbon footprints. Solar energy, for example, grew by 22% in capacity globally in 2020 (IEA).
-
Energy Efficiency: Innovations such as LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, and advanced building materials help reduce energy consumption.
-
Waste Management: Green tech is revolutionizing waste management through recycling, composting, and converting waste into usable resources. These practices reduce landfill waste and conserve natural resources.
-
Water Purification: Technologies focused on water filtration, desalination, and wastewater management ensure clean water supplies and sustainable water usage.
-
Sustainable Transportation: Electric vehicles, hybrid cars, and sustainable public transportation options are critical in reducing emissions from the transportation sector.
Top 8 Green Tech Innovations
Green technology innovations continue to reshape industries and contribute significantly to sustainability goals. Here are the Top 8 Green Tech Innovations making a real difference:
-
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS): Capturing and storing carbon dioxide to reduce emissions from industrial sources is a growing field. The Global CCS Institute reports over 40 million tonnes of CO2 captured annually by operational facilities.
-
Electric Vehicles (EVs): As global EV sales surged by 41% in 2020 (ICCT), electric cars continue to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower emissions from the transportation sector.
-
Vertical Farming: This innovative farming technique involves growing crops in stacked layers, often in controlled environments. Vertical farming uses up to 95% less water than traditional farming and yields significantly more per square meter.
-
Green Architecture/Building: Sustainable building practices, such as using energy-efficient materials and designs, are transforming the construction industry. LEED-certified buildings have significantly reduced CO2 emissions globally.
-
Renewable Energy Sources (Solar, Wind, Hydro): Solar power alone has seen a remarkable 18-fold increase in installations from 2009 to 2020 (SEIA), illustrating the shift towards clean, renewable energy.
-
Biomimicry: Innovations inspired by nature, such as self-cleaning surfaces (the Lotus Effect) and termite mound-inspired cooling systems, are revolutionizing design and architecture.
-
Green Cities: Cities like Copenhagen and San Francisco are integrating renewable energy, green spaces, and sustainable transportation to create carbon-neutral urban environments by 2050.
-
Plant-Based Packaging: Alternatives to plastic packaging made from renewable biological sources, such as bioplastics, are gaining traction. European Bioplastics projects a 36% increase in bioplastics production capacity by 2024.
Challenges in Green Technology
Despite the promising advancements in green tech, several challenges hinder widespread adoption and implementation:
-
High Initial Costs: Green technologies often require significant upfront investments, which can be prohibitive for businesses and consumers. Solar PV installations, for example, can cost between $850 and $1,000 per kilowatt.
-
Technological Barriers: Many green technologies, such as efficient energy storage and carbon capture, are still in development stages and face technical limitations.
-
Regulatory and Policy Hurdles: Inconsistent regulations across countries can slow the adoption of green technologies. Lack of incentives in some regions also poses a barrier.
-
Market Acceptance: Shifting consumer behaviors and perceptions toward sustainability can take time. Many people remain reluctant to invest in green tech if the cost is higher than traditional options.
-
Infrastructure Deficiencies: Insufficient infrastructure, such as charging stations for electric vehicles and renewable energy grid integration, remains a significant barrier to the scalability of green tech solutions.
Future Outlook on Green Tech
The future of green technology is bright, with growing investments, ongoing research, and supportive policies paving the way for widespread adoption. Key trends shaping the future include:
-
Advancements in Renewable Energy: The IEA projects that renewables will account for nearly 95% of the global increase in power capacity through 2025, with solar and wind leading the charge.
-
Energy Storage Solutions: Battery technologies are evolving, with solid-state batteries expected to increase storage capacity and efficiency significantly.
-
Smart Grids: The integration of smart grids will optimize energy distribution and allow greater incorporation of renewable energy sources.
-
Green Hydrogen: Green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy, is emerging as a key player in decarbonizing industries and transportation.
-
Circular Economy Models: Focusing on reducing waste and reusing resources, circular economy models aim to achieve a sustainable, low-carbon future.
Do the Benefits Outweigh the Costs?
While green tech aims to reduce harm, it’s not without trade-offs:
-
EV batteries require lithium, often mined in ecologically sensitive regions.
-
Hydropower affects aquatic ecosystems.
-
Solar panels and wind turbines depend on rare earth minerals, which can involve environmentally harmful extraction processes.
Thus, while green tech is preferable to traditional methods, a life-cycle assessment is essential to ensure the net environmental benefit.
Green technology is a powerful tool in the fight against climate change and environmental degradation. From energy-efficient buildings to electric vehicles and renewable energy, the innovations driving the green tech sector are shaping a sustainable future. While challenges remain, the continued advancement of green technologies promises a transformative shift toward a more sustainable, eco-friendly world.
As we look ahead, green tech will continue to play a pivotal role in reducing environmental impact, conserving resources, and promoting sustainability across industries. The journey toward a greener future is ongoing, but with innovation and collective effort, the goal is within reach.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.