In an era where our lives are increasingly digitised, cybersecurity is no longer a niche concern reserved for tech experts—it's a universal necessity. Whether you're an individual sharing personal information online or a multinational company safeguarding sensitive data, staying ahead of evolving cyber threats is crucial. The digital battleground is constantly shifting, and understanding the emerging trends in cybersecurity can empower organisations and individuals alike to defend themselves effectively.
Also read: What’s Next in Cyber Security? 10 Big Trends and Surprising Challenges in 2025
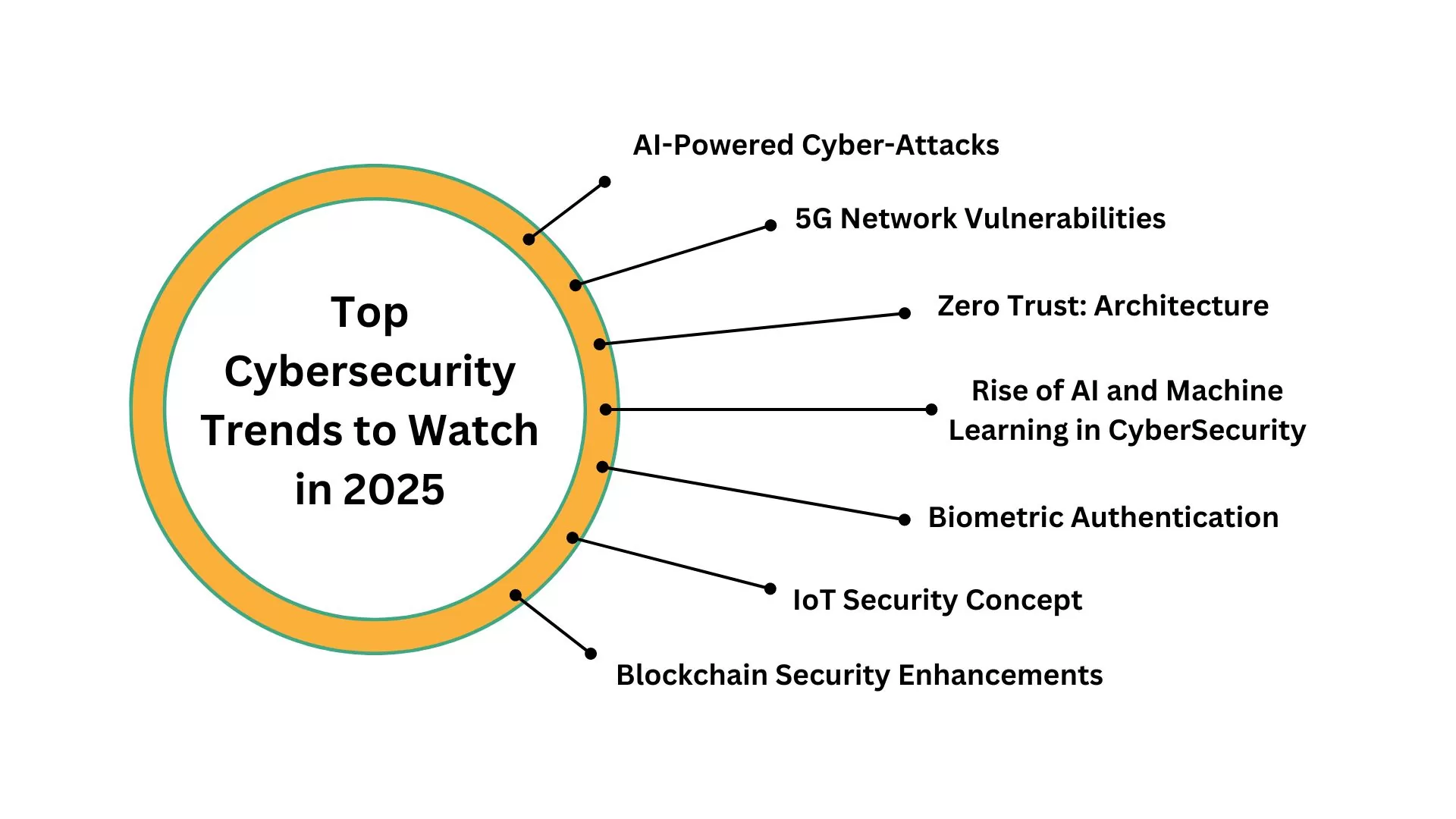
10 Powerful Trends That Will Shape Our Digital Future
1. AI and Machine Learning: The Double-Edged Sword
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) revolutionise cybersecurity by enabling faster threat detection, automated responses, and predictive analysis. AI can analyse vast amounts of data in real-time to detect anomalies that might indicate a cyberattack, allowing organisations to act before damage is done.
However, the same technology is also being exploited by cybercriminals. AI-powered phishing attacks, deepfake scams, and automated malware distribution are on the rise. As defenders and attackers both leverage AI, it becomes a technological arms race that pushes cybersecurity professionals to stay one step ahead.
Why it matters: AI is not just a tool but a critical frontline asset. Organisations investing in AI for cybersecurity are better equipped to detect zero-day threats and respond swiftly.
2. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): Trust Nothing, Verify Everything
The traditional security model assumed that anything inside the network could be trusted. But with increasing insider threats, remote work, and sophisticated breaches, the "trust but verify" model has become obsolete. Enter Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA).
ZTA is based on the principle of "never trust, always verify." It continuously validates every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location within the network.
Why it matters: Zero Trust significantly reduces the risk of internal and external breaches. It's especially vital for remote and hybrid work environments where secure perimeter-based security is no longer sufficient.
3. Rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Ransomware has evolved from random attacks to an organised industry. Today, cybercriminals offer Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) on the dark web, allowing even low-skilled attackers to launch sophisticated attacks. These services provide user-friendly dashboards, customer support, and even revenue-sharing models.
The increasing availability and profitability of RaaS have led to a surge in ransomware attacks on healthcare, finance, education, and government sectors.
Why it matters: With critical infrastructure under threat, organisations must strengthen backup protocols, employee training, and endpoint protection strategies to guard against ransomware.
4. Cloud Security Takes Centre Stage
The global shift to cloud computing—accelerated by the pandemic—has made cloud security a top priority. While the cloud offers scalability and convenience, it also presents new vulnerabilities. Misconfigured storage, lack of visibility, and shared responsibility models can expose sensitive data.
Cloud-native security tools, such as Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP), are now essential in identifying risks and ensuring compliance.
Why it matters: As more businesses migrate to the cloud, having a proactive cloud security strategy is crucial to avoid data leaks, service outages, and compliance violations.
5. Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA): Decentralised and Dynamic
Cybersecurity Mesh is an architectural approach that allows security policies to be enforced across distributed networks and environments. Instead of securing a single perimeter, CSMA ensures security is woven throughout every part of an IT infrastructure.
It provides a more modular and scalable framework, especially important for enterprises with complex, hybrid systems.
Why it matters: CSMA enhances flexibility and resilience. By treating each device or network node as its own security perimeter, it allows organisations to respond more dynamically to threats.

6. Human-Centric Security: Training and Awareness
Despite technological advancements, human error remains one of the biggest vulnerabilities in cybersecurity. Phishing emails, weak passwords, and social engineering attacks continue to exploit the human element.
Companies are now investing in more interactive and personalised cybersecurity awareness programs to foster a security-first mindset among employees.
Why it matters: A well-informed employee can be the first line of defence. Human-centric approaches reduce insider threats and improve overall security posture.
7. Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy
With data breaches becoming more common, governments and regulatory bodies are imposing stricter data protection laws. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) in India, and similar frameworks globally demand transparency, accountability, and consumer rights.
Organisations must adapt by strengthening data governance and ensuring compliance to avoid hefty penalties and reputational damage.
Why it matters: Compliance is not just a legal obligation but also a trust-building measure that boosts customer confidence and brand integrity.
8. Post-Quantum Cryptography: Preparing for the Next Frontier
Quantum computing poses a potential threat to current encryption standards. While still in its infancy, quantum computers could, in theory, break traditional encryption in seconds.
Post-quantum cryptography is an emerging field focused on developing algorithms resistant to quantum attacks. Governments and institutions are already exploring quantum-safe cryptographic solutions to future-proof digital security.
Why it matters: Being quantum-ready will be essential in the coming decade to protect national security, financial transactions, and personal data from next-generation cyber threats.
9. Extended Detection and Response (XDR): Holistic Threat Management
XDR solutions integrate data from multiple security products—endpoints, networks, servers, and emails—to provide a unified view of threats. This consolidated approach enhances threat detection accuracy and speeds up response times.
Unlike traditional SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), XDR is proactive, offering contextual insights and automated mitigation.
Why it matters: In a world of overwhelming alerts and false positives, XDR helps security teams focus on what truly matters—real threats with real consequences.
10. Security for the Internet of Things (IoT)
The explosion of IoT devices—from smart homes to industrial sensors—has expanded the attack surface exponentially. Many of these devices lack proper security protocols, making them easy targets.
Securing IoT involves implementing network segmentation, firmware updates, and device authentication to prevent them from becoming entry points for larger attacks.
Why it matters: As we become more connected, every smart device is a potential risk. IoT security is crucial for both personal safety and national infrastructure resilience.
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity is no longer just an IT issue—it's a fundamental pillar of digital trust, economic stability, and national security. The trends shaping the future of digital defence reveal a complex, high-stakes landscape where adaptability, awareness, and innovation are key.
From the rise of AI to the looming threat of quantum computing, the battle for digital security is multifaceted and fast-evolving. Organisations must take a proactive, layered approach—investing in technology, training, and forward-looking strategies to stay ahead of the curve.
Because in the digital age, the question is not if a cyberattack will happen, but when. And when it does, being prepared makes all the difference.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.










