In an era where data is gold and cybercriminals evolve faster than legislation, staying ahead of cybersecurity trends is not a luxury—it's a necessity. With over 30,000 vulnerabilities disclosed globally in the past year alone (a 17% jump from the previous year), the cyber threat landscape for 2025 demands not just awareness but actionable readiness.
Whether you’re a small business or a multinational enterprise, understanding the latest cyber security trends, and more importantly, the challenges in adopting them, will define your ability to protect assets, users, and reputation in a digitally-driven world.

What Are Cyber Security Trends?
Cyber security trends refer to emerging tactics, technologies, and threats shaping the digital threat landscape. These trends reflect the constant evolution of attacker capabilities, global events, and tech adoption—from AI-driven malware to quantum computing.
As digital transformation accelerates and remote work becomes permanent, cyber attackers find more entry points. Thus, organizations must proactively monitor these developments, not only to protect their IT environments but also to maintain trust, ensure compliance, and manage financial risks.
Why Cyber Security Trends and Challenges Matter More Than Ever
-
Attack Complexity Has Evolved: From fileless malware to multi-stage attacks, threat actors today bypass traditional defenses easily. Static, signature-based tools alone no longer suffice.
-
Brand Reputation is on the Line: A single high-profile breach can cost millions and permanently damage trust among customers, partners, and investors.
-
Regulations Are Getting Tougher: From GDPR to HIPAA, regulatory frameworks now impose steep penalties for non-compliance, forcing organizations to modernize fast.
-
Remote Work Expands the Attack Surface: Home networks, mobile devices, and cloud tools increase vulnerabilities—making endpoint security and secure VPNs essential.
-
Financial Stakes Are Higher: The cost of ransomware attacks has reached an average of USD 2.73 million per incident. Indirect losses like downtime and reputational damage add even more weight.
-
Vulnerability Management Is a Race Against Time: With thousands of vulnerabilities published yearly, patch management is a race to prevent exploits before attackers capitalize.
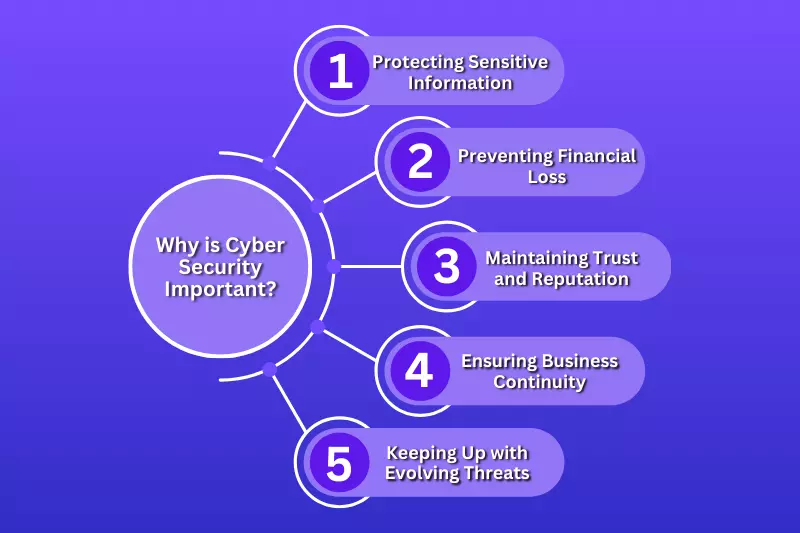
Top 10 Cyber Security Trends for 2025
1. AI-Driven Malware
Cybercriminals are now leveraging machine learning to mutate malware in real-time, bypassing sandbox environments and traditional AV tools. The result? AI vs. AI cyber warfare, where defenders must use anomaly detection to stay in the game.
2. Zero Trust Architectures
The “trust nothing, verify everything” model is rapidly replacing outdated perimeter defenses. Micro-segmentation, session revalidation, and strict access controls are now at the core of secure enterprise networks.
3. Quantum Computing Threats
Quantum decryption is not a sci-fi concept anymore. Encrypted data intercepted today could be decrypted tomorrow. This fuels the adoption of post-quantum cryptography and quantum-safe algorithms.
4. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Professional cybercrime groups now offer plug-and-play ransomware kits to less skilled affiliates, increasing the number and severity of attacks. Offline backups and segmented networks are essential deterrents.
5. 5G and Edge Security Risks
With the rise of IoT and real-time edge computing, 5G infrastructures pose new vulnerabilities. Supply chains, healthcare systems, and industrial controls are especially at risk.
6. Insider Threats Amplified by Hybrid Work
From careless data sharing on collaboration tools to disgruntled employees stealing IP, insider risks are growing. Tools using behavioral analytics and DLP (data loss prevention) are critical safeguards.
7. Supply Chain Attacks
Events like SolarWinds highlighted the domino effect of one weak vendor. Expect tighter contract clauses and continuous monitoring of third-party integrations as standard practices.
8. Cloud Container Vulnerabilities
Containers speed up deployment—but if misconfigured, they can open backdoors. Security must now be embedded directly into DevOps pipelines, aka “shift-left” security.
9. Social Engineering via Deepfakes
Deepfake videos and audio scams impersonate executives to trick employees into fraudulent transfers. Awareness training and verification protocols are non-negotiable defenses.
10. Convergence of IT and OT Security
As industrial systems connect to IT networks (Industry 4.0), traditional air-gaps disappear. Joint monitoring of IT and OT systems becomes mandatory to prevent disruptions in critical infrastructure.

Challenges in Adopting These Trends
While the urgency to modernize security is clear, organizations face a labyrinth of challenges when attempting to implement the latest cyber security trends.
Limited Budgets
Smaller businesses, in particular, struggle to justify upfront costs of advanced detection tools or security talent. However, the long-term cost of a breach is often exponentially higher than the cost of prevention.
Talent Shortages
There’s a global deficit in cybersecurity professionals. The lack of skilled threat hunters, analysts, and DevSecOps experts stalls implementations of frameworks like zero trust or AI-powered analytics.
Multi-Cloud Complexity
Running workloads across AWS, Azure, and GCP creates visibility silos. Unified patching, access control, and monitoring across these platforms are harder than they seem.
Cultural Resistance
Security changes—like multi-factor authentication or privilege restrictions—can cause friction. Without leadership buy-in and employee education, users may disable or work around new safeguards.
Data Privacy and Governance
Advanced threat detection requires data aggregation, but this must be balanced against privacy laws and ethical concerns. Anonymization and clear policy boundaries help bridge the gap.
Legacy System Dependencies
Outdated systems, especially in government and finance, are difficult to replace but easy to exploit. Phasing them out without disrupting operations remains a top challenge.
Practical Implications of Implementing Trends
AI-Powered Threat Hunting
Combining AI with human analysts accelerates breach detection and reduces alert fatigue. Aggregating logs from multiple sources allows faster anomaly flagging and incident response.
Automated Patch Management
Automation of patches across OS, apps, and IoT devices removes human error and accelerates vulnerability mitigation—although testing is still required to avoid software conflicts.
Secure-by-Design Development
Embedding security in the development lifecycle—from code scanning to threat modeling—ensures fewer vulnerabilities make it to production. This proactive defense cuts costs and audit time.
Encryption and Micro-Segmentation
By dynamically encrypting data and segmenting networks, lateral movement is blocked, even if attackers gain initial access. This is essential for multi-cloud security.
IAM 2.0 and Zero Trust Identity
New IAM systems include risk-based authentication, biometrics, and continuous session validation. This reduces dependency on passwords and limits privilege misuse.
SOC Automation
Security Operation Centres (SOCs) are automating tasks like IP blocking and alert triage to focus human efforts on complex attacks. This ensures faster, consistent responses.
How to Prepare for the Cyber Threat Landscape of 2025
1. Continuous Risk Assessments: Constantly scan, pen test, and audit your infrastructure. Real-time insights help prioritize what to fix before it's exploited.
2. Build a Culture of Security: Technology is only as strong as its users. Run phishing simulations, explain the “why” behind policies, and gamify security awareness.
3. Strengthen Cloud Governance: Apply consistent policies, enforce MFA, and unify monitoring dashboards across all cloud platforms. Visibility across hybrid environments is critical.
4. Share Threat Intelligence: Collaborate with industry peers and intelligence networks. Shared indicators of compromise (IoCs) help defend against zero-day attacks faster.
5. Have an IR Plan: Create and regularly test incident response playbooks. Tabletop exercises prepare your team to respond swiftly and cohesively under real attack scenarios.
6. Commit to Iteration and Innovation: Adopt quantum-safe encryption, next-gen UEBA, and advanced monitoring solutions. Drop legacy limitations and keep your architecture nimble.
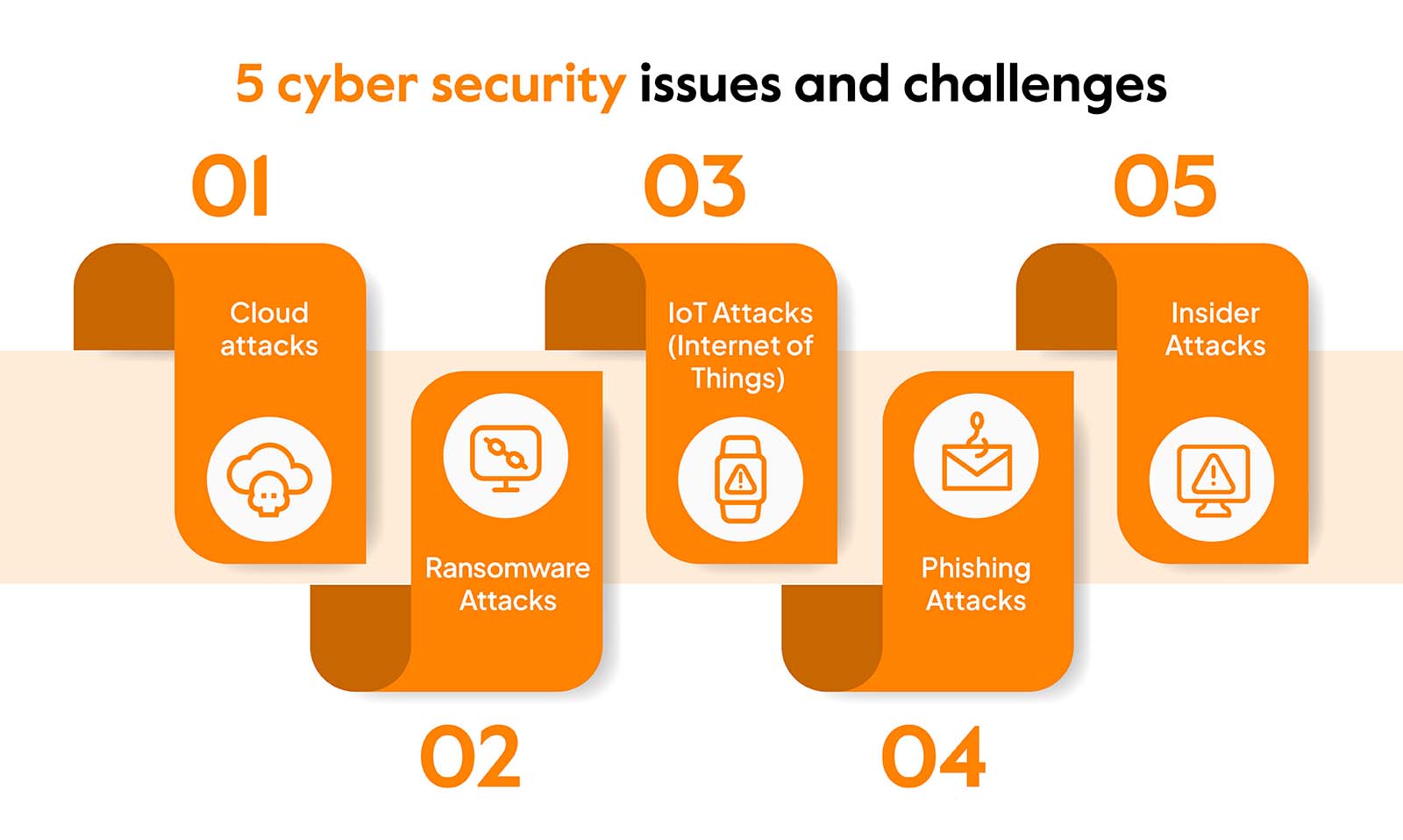
Sector-Specific Focus: Where Threats Hit Hardest
-
Healthcare: Patient data is a prime target. Zero trust and endpoint encryption are must-haves, especially with telemedicine and HIPAA compliance.
-
Finance: Banks and fintech firms face phishing, credential theft, and account manipulation. AI-driven fraud detection and real-time transaction analysis are critical.
-
Retail & E-Commerce: Card skimming and bot attacks spike during sales. DevSecOps and Web Application Firewalls (WAF) are key tools for defense.
-
Public Sector: Budget-strapped agencies house sensitive citizen data. They must rely on zero trust frameworks, endpoint monitoring, and partnerships with security vendors.
-
Manufacturing & Industrial IoT: As OT and IT converge, compromised devices can halt production or manipulate outputs. Specialized OT monitoring tools and segmentation strategies are essential.
The Future Is Now—Are You Ready?
Cyber security in 2025 is no longer about if an organization will be targeted, but when—and how prepared it will be. From AI-powered malware to deepfake social engineering, attackers are more capable than ever. But with proactive strategies, robust architectures, and a culture of awareness, defenders can stay one step ahead.
It’s not just about technology—it’s about resilience. That means embracing innovation, breaking silos, educating employees, and constantly refining your defense posture. In a world of growing digital dependencies, preparedness is the strongest perimeter you can build.
With inputs from agencies
Image Source: Multiple agencies
© Copyright 2025. All Rights Reserved Powered by Vygr Media.